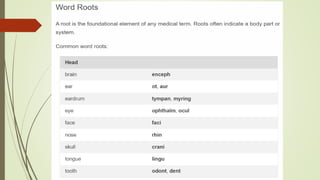
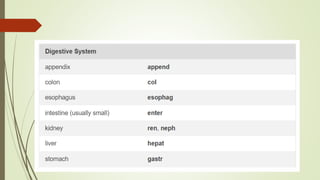
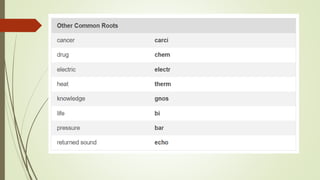
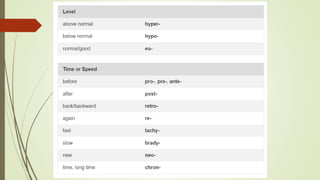
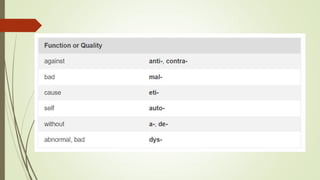
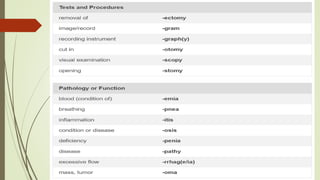
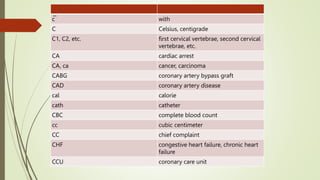
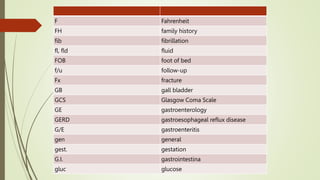
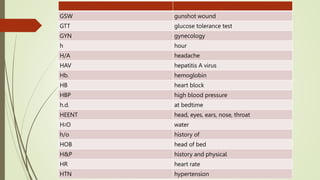
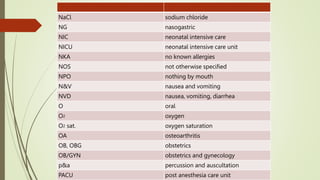
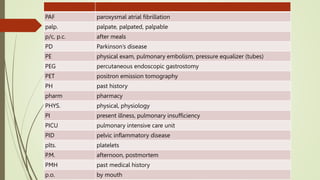
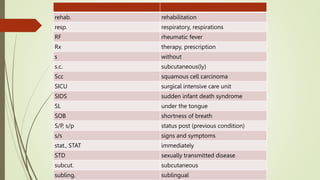
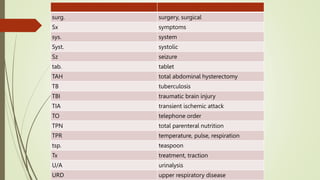
Medical terminology is used to describe anatomical structures, medical processes, conditions, procedures, and treatments. Most medical terms follow a standard structure consisting of a prefix, root, and suffix. Prefixes usually indicate a location or type, roots provide the essential meaning, and suffixes specify a function, disorder, or status. Understanding this structure and common prefixes, roots, and suffixes allows the meaning of thousands of medical terms to be deduced. Common medical abbreviations are also presented to facilitate communication between medical professionals.