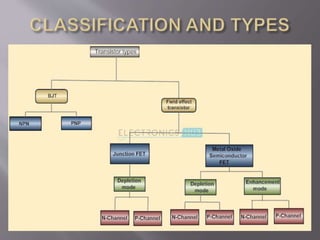
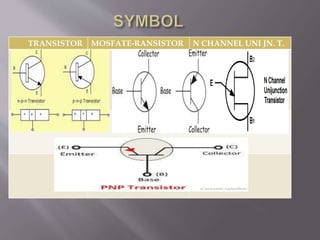
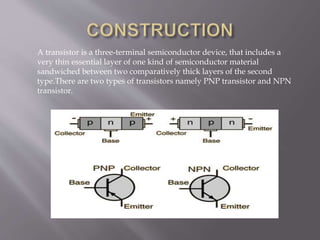
John Bardeen, Walter Brattain and William Shockley invented the first working transistors at Bell Labs in 1947 and 1948. They created the point-contact transistor in 1947 and the bipolar junction transistor in 1948. A transistor is a semiconductor device with three terminals that can amplify or switch electronic signals and current. It consists of a thin layer of semiconductor material sandwiched between two thicker layers of a different semiconductor type. There are two main types: PNP and NPN transistors. Transistors are used as amplifiers to boost current and signals and as switches to turn circuits on and off. They are fundamental components in integrated circuits.