Embed presentation
Download to read offline





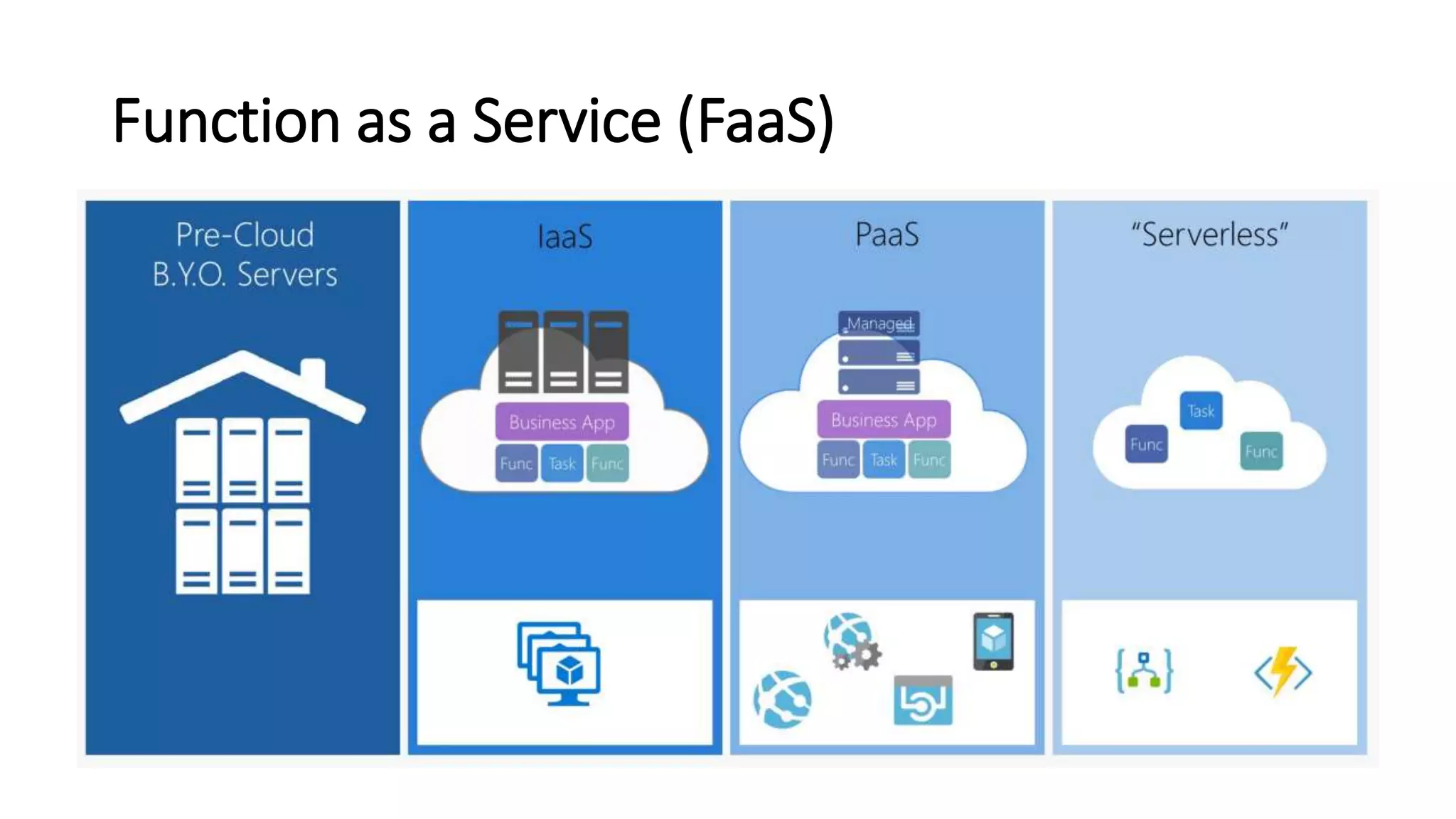

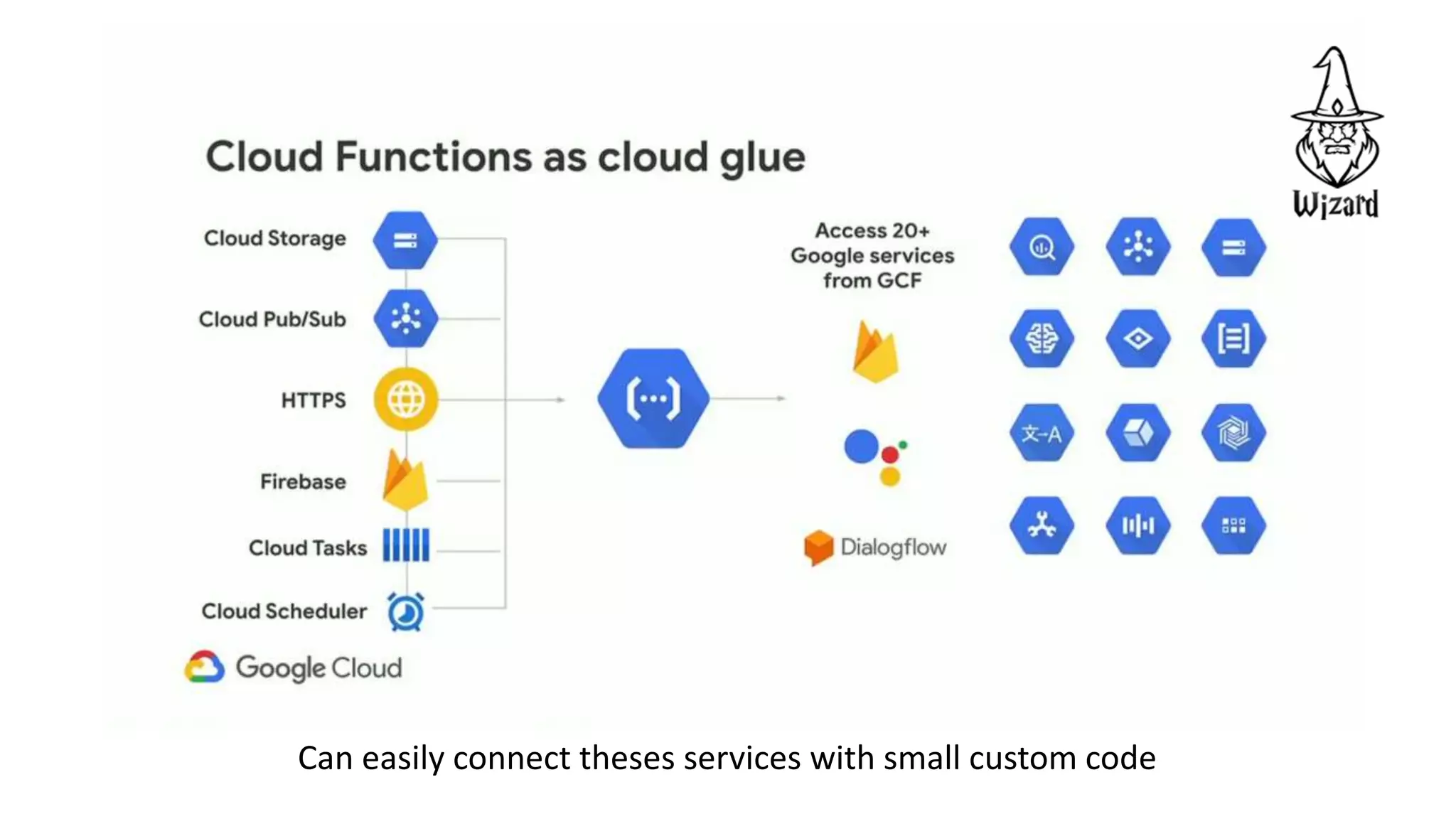



The document discusses serverless computing, highlighting its characteristics such as automatic scaling, precise usage-based costs, and high availability. It emphasizes the benefits of using Function as a Service (FaaS), including reduced server management and increased productivity for developers. Use cases for FaaS are provided, indicating suitable applications and limitations.










