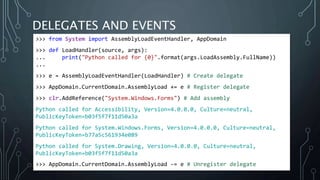
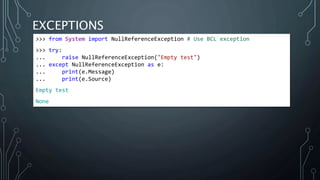
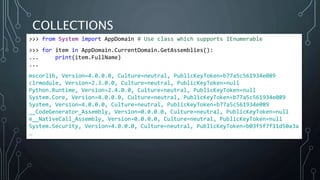
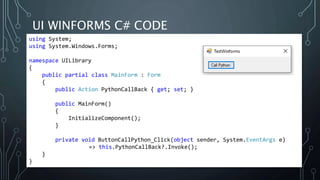
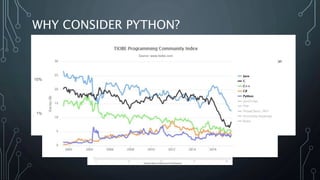
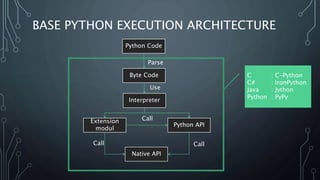
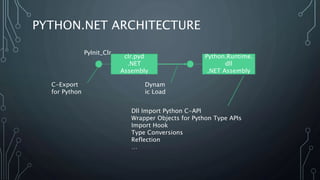
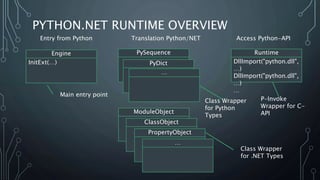
The document introduces Python.NET, a tool that allows integration of .NET libraries with Python through an extension module, maintaining a rich history of development from 2005 to the present. It details the architecture, primary functionalities, and the dynamic interaction between Python and .NET, including accessing and manipulating .NET types within Python scripts. Additionally, it provides examples of usage patterns for creating user interfaces and handling events in a .NET context using Python.









 # Use overloaded constructor
>>> s # display class
<System.String object at 0x0000020A5FF64908>
>>> print(s) # Use ToString method
AAAAAAAA
>>> from System.Collections.Generic import Dictionary # Import used types
>>> d = Dictionary[String, String]() # Use generic constructor
>>> d2 = Dictionary[str, str]() # Use auto mapped types
>>> print(d) # Use ToString method
System.Collections.Generic.Dictionary`2[System.String,System.String]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontopythonnet-171012085420/85/Introduction-to-Python-Net-14-320.jpg)
![INDEXERS, ARRAYS
>>> from System.Collections.Generic import Dictionary as d
>>> jagged = d[str, d[str, int]]() # Create dict of dicts
>>> jagged["a"] = d[str, int]()
>>> jagged["a"]["b"] = 10
>>> jagged["a"]["b"]
10
>>> from System import Array
>>> a = Array[int]([2,2])
>>> a
<System.Int32[] object at 0x0000020A5FF838D0>
>>> a[0] # Multidimensional a[1,1]
2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontopythonnet-171012085420/85/Introduction-to-Python-Net-15-320.jpg)