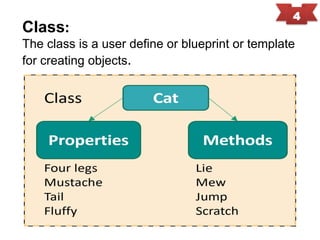
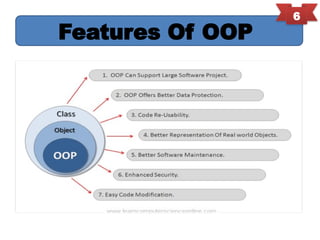
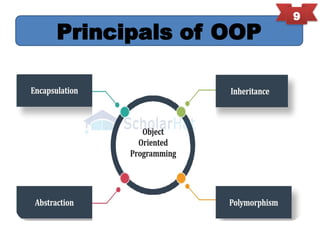
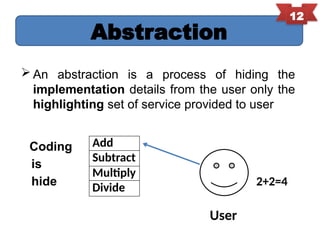
Object-oriented programming (OOP) is a programming paradigm that organizes software design around data or objects, enhancing code reusability, maintainability, and modularity. Key principles of OOP include encapsulation, abstraction, inheritance, and polymorphism, with significant contributions from early languages like Simula and Smalltalk. The document provides an overview of these principles along with historical context and examples.