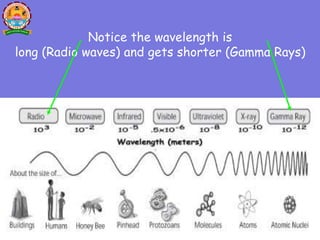
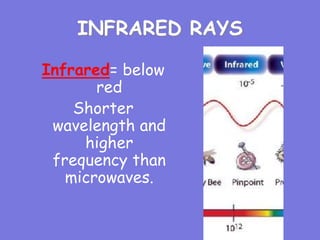
Wireless communication transfers information between devices without a physical connection using electromagnetic waves across the electromagnetic spectrum. Wireless signals are transmitted using antennas and received by antennas connected to other devices. The electromagnetic spectrum ranges from long radio waves to short gamma rays, with different frequencies and wavelengths used for different wireless technologies. Common uses of the electromagnetic spectrum include radio, GPS, WiFi, radiation therapy, and X-rays.