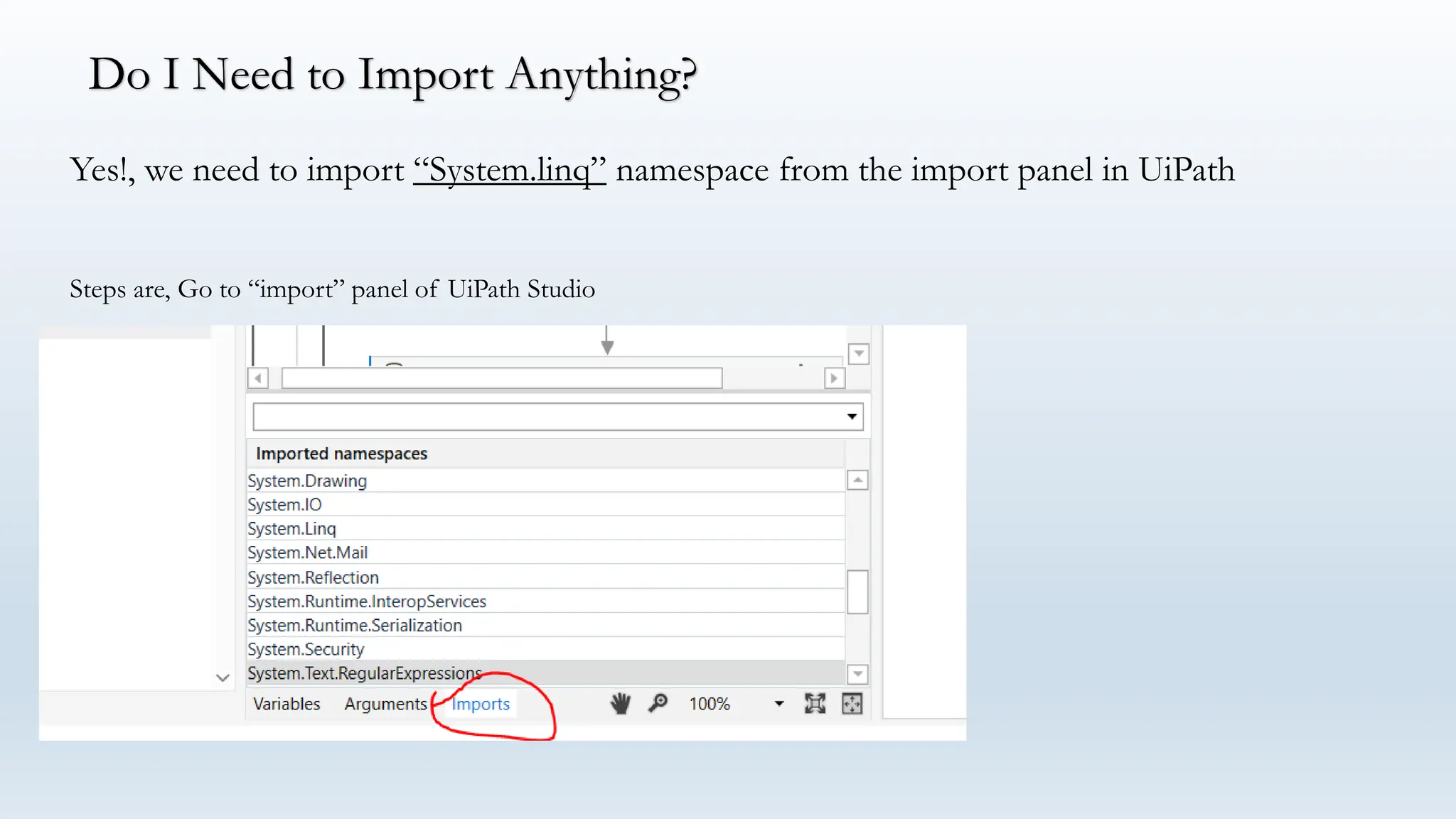
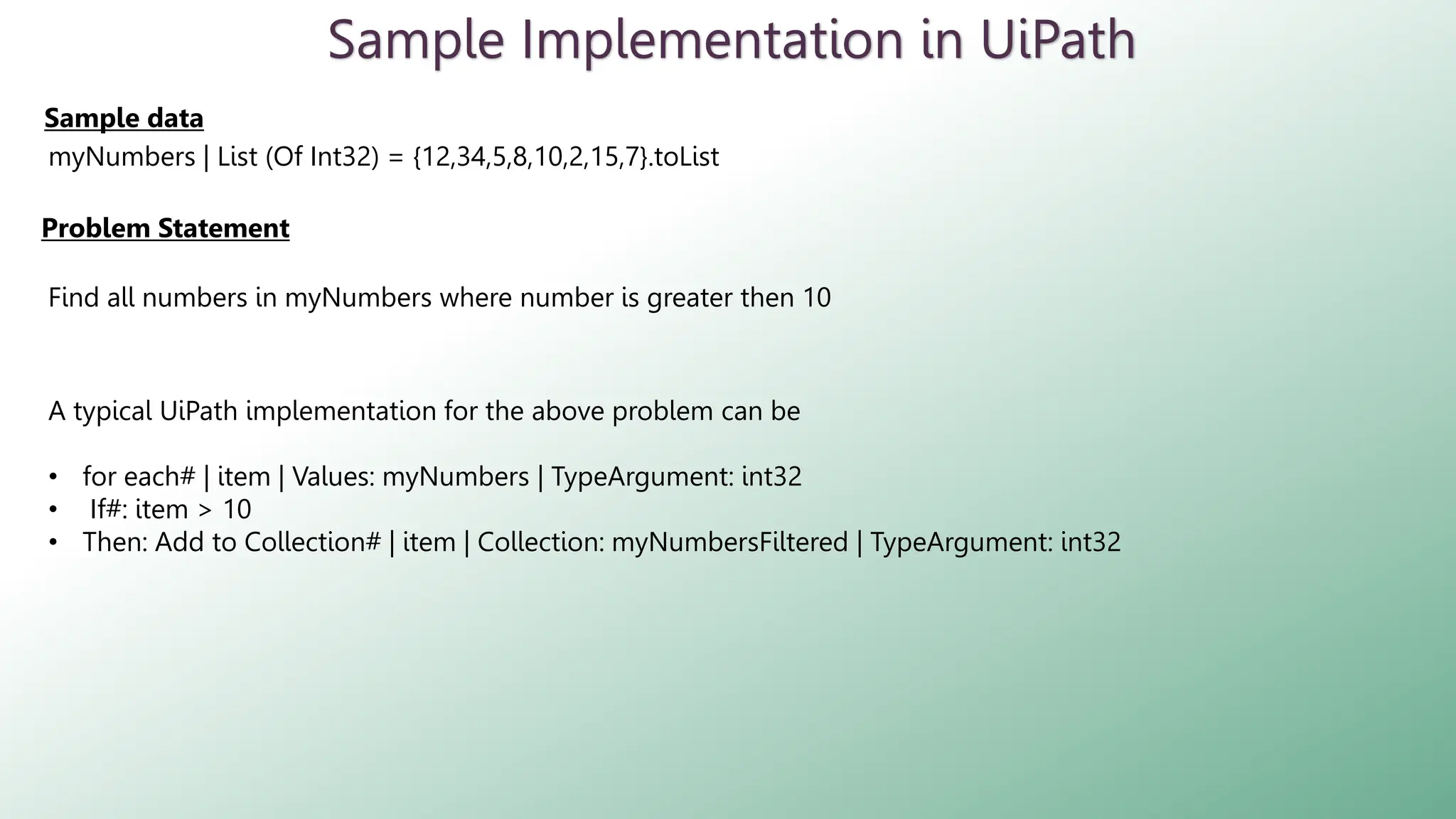
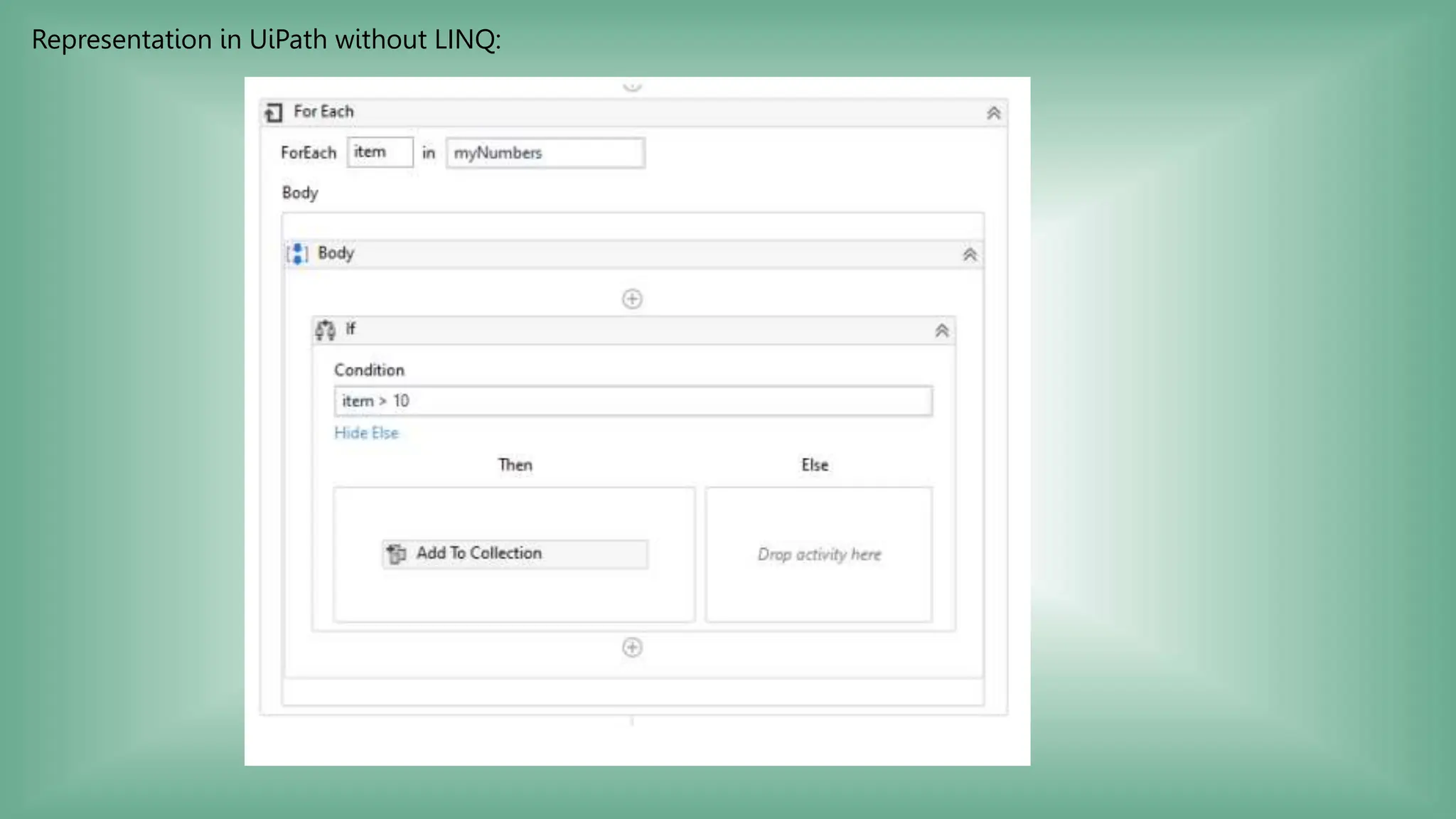
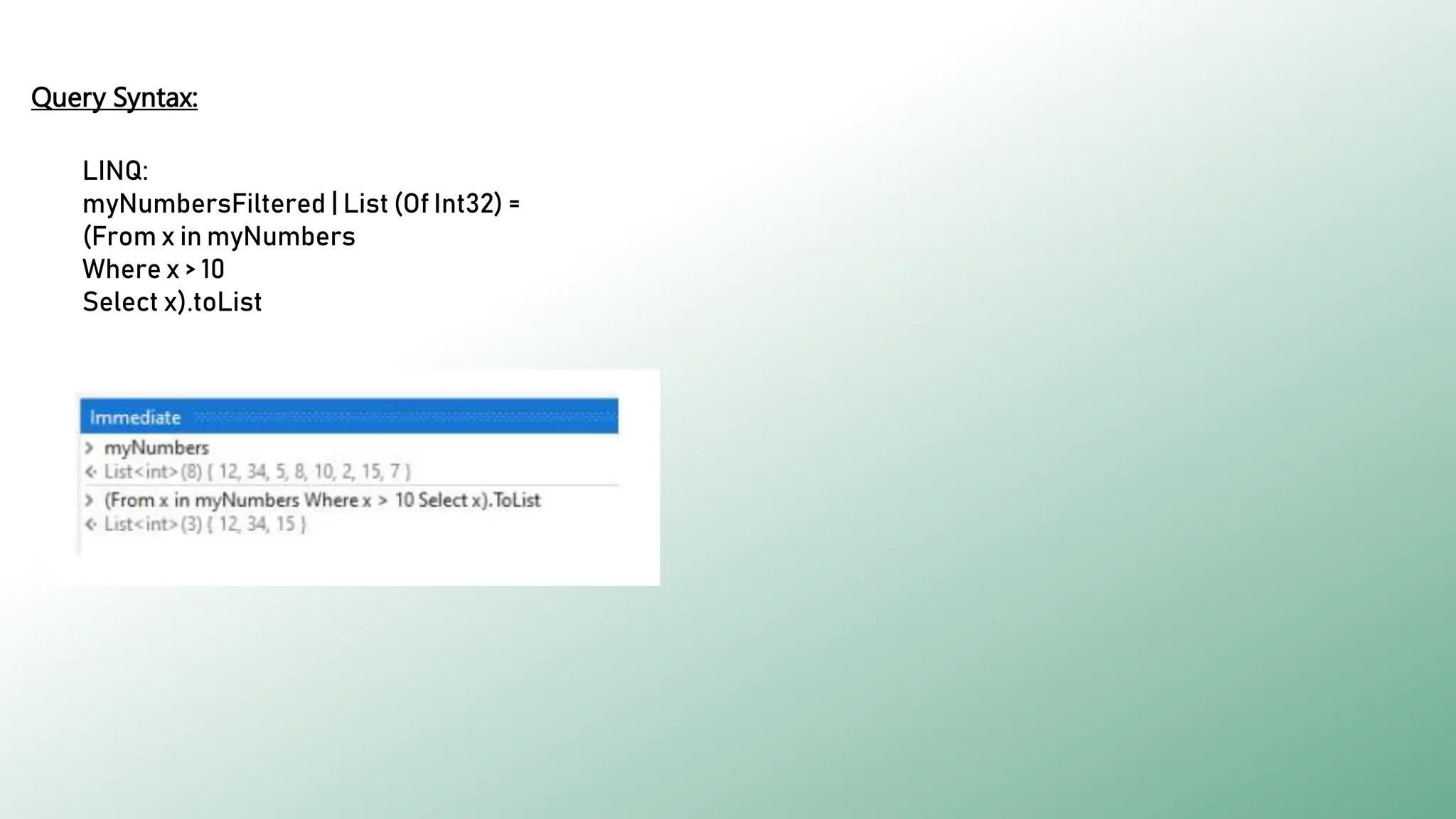
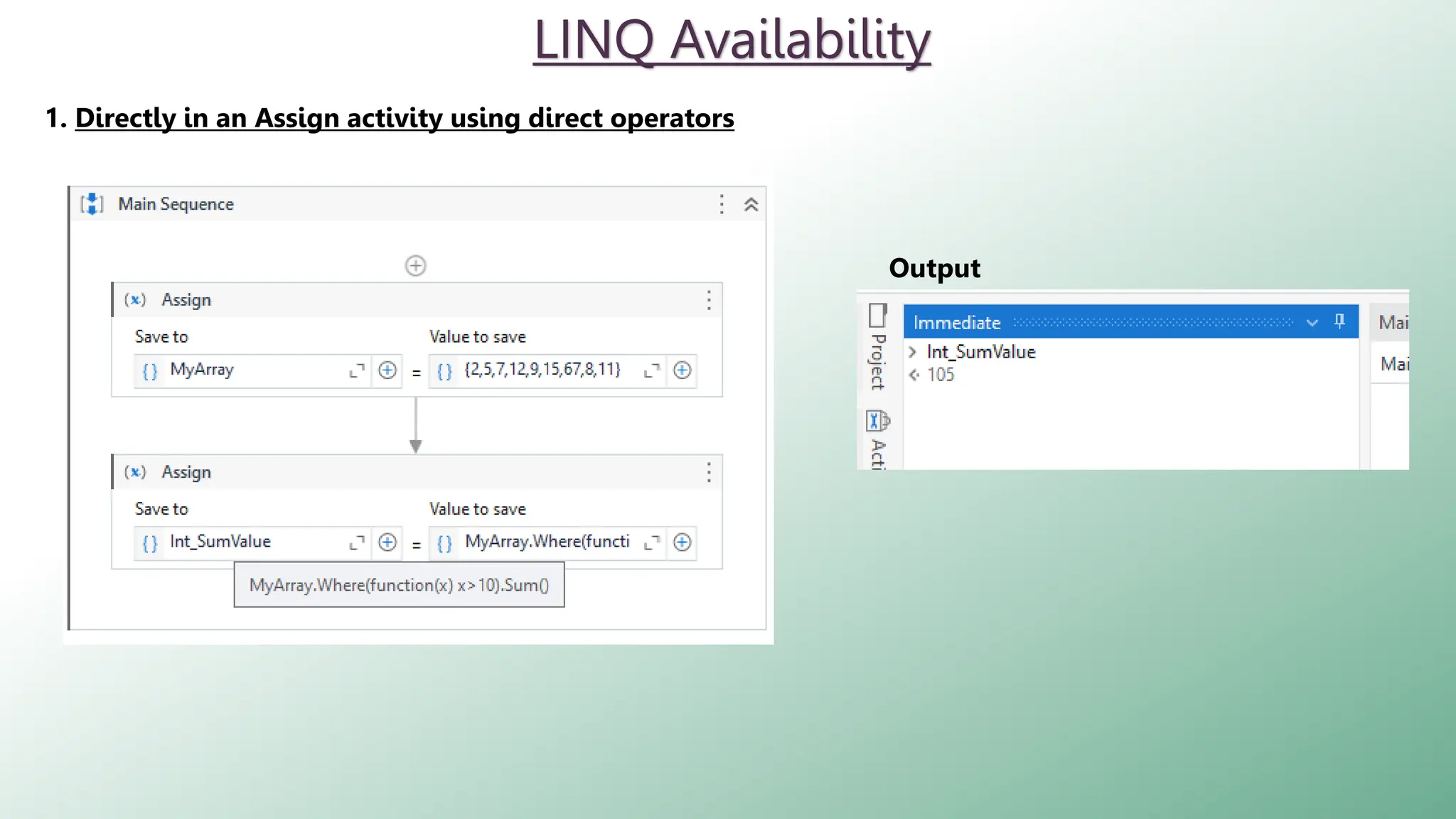
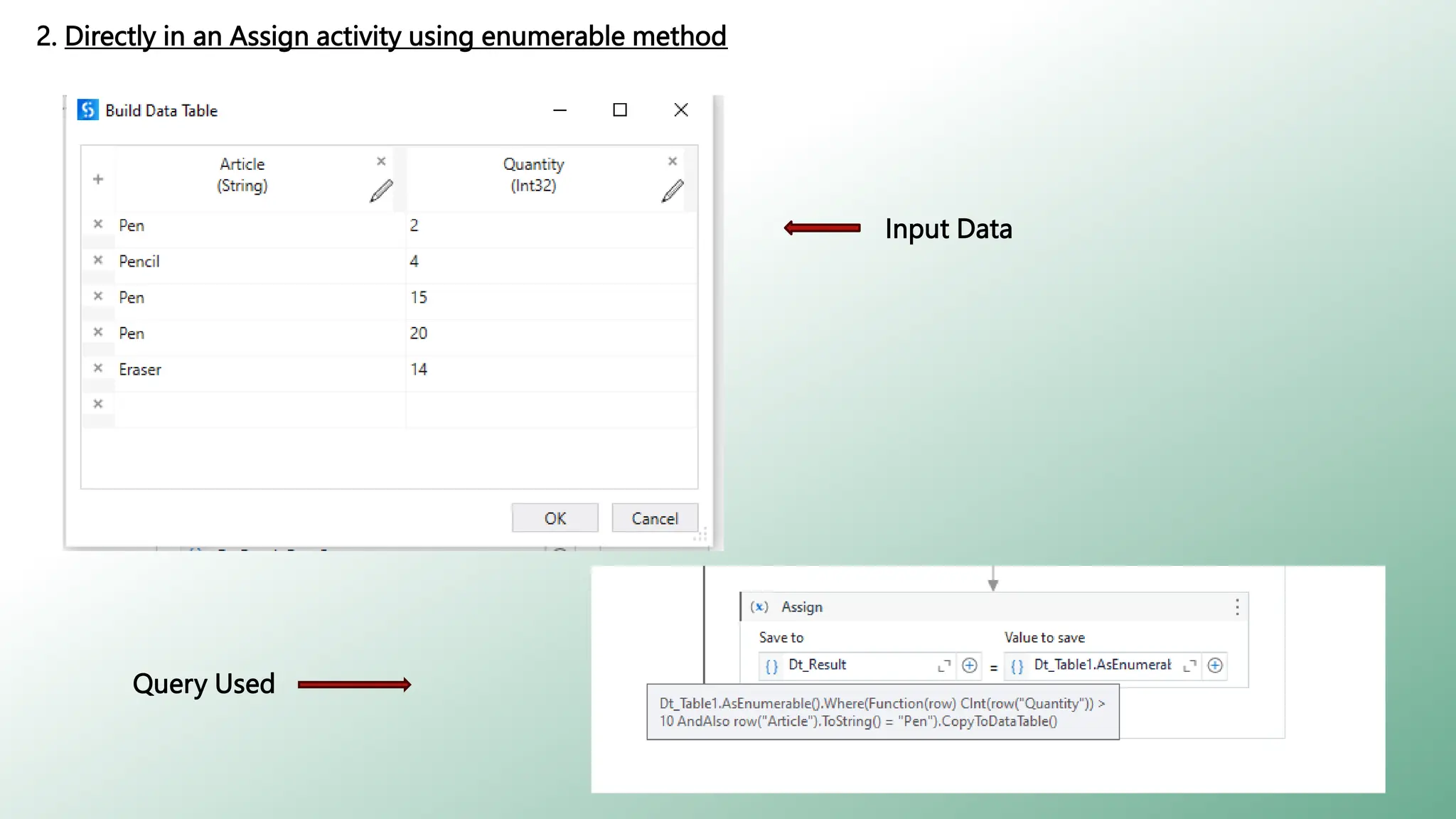
LINQ (Language Integrated Query) is a feature in C# and VB.NET for querying various data sources like collections, DataTables, XML, and web services. It enables efficient data processing with capabilities such as filtering, grouping, sorting, and aggregation using method and query syntax. In UiPath, using LINQ enhances data manipulation tasks by allowing developers to construct queries in a more readable format.