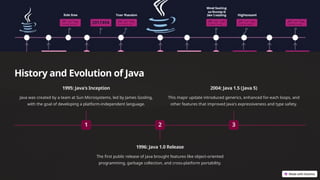
The document provides an overview of Java, a versatile programming language known for its portability and strong object-oriented features. It covers the history of Java, core syntax, and key concepts such as object-oriented programming, control structures, and packages. Additionally, it highlights various applications of Java including web, mobile, and enterprise development, along with best practices for effective Java programming.