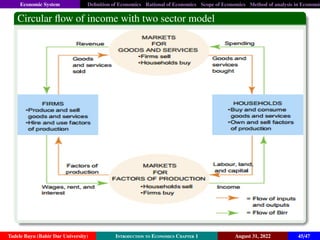
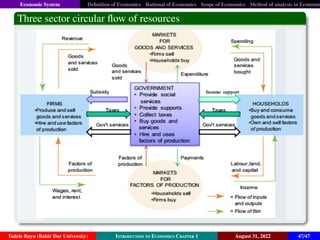
The document is an introduction to economics, providing definitions, rationales, scope, and methods of analysis. It discusses various economists' perspectives on economics, emphasizing scarcity, choice, opportunity cost, and the production possibilities frontier. Ultimately, it defines economics as the study of efficient allocation of scarce resources to meet unlimited human needs.