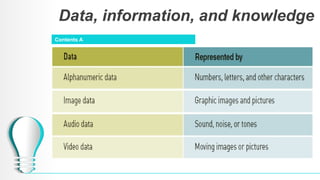
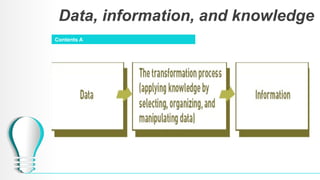
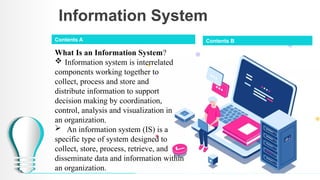
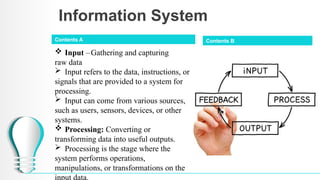
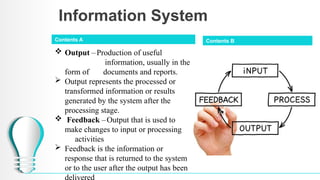
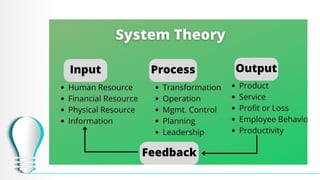
The document outlines a course on database systems, covering foundational concepts like data, information, knowledge, and information systems. It explains the processes involved in converting raw data into meaningful information and details various types and components of information systems. The course also includes quizzes to assess understanding of these concepts.