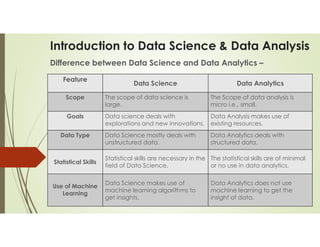
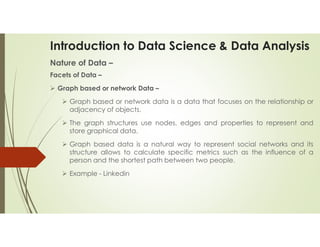
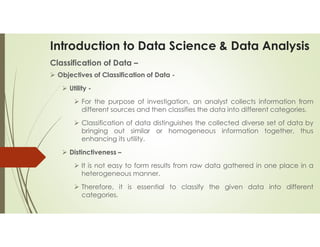
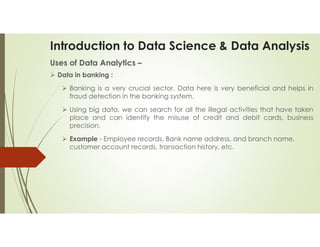
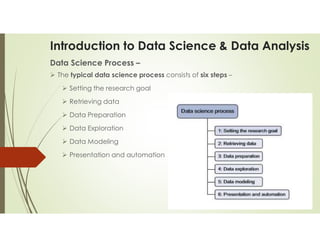
Data science and data analytics are related fields focused on extracting knowledge from data, but they have distinct focuses. Data science is a broader, interdisciplinary field that encompasses data analytics and includes activities like machine learning, algorithm development, and predictive modeling. Data analytics, on the other hand, is more focused on analyzing past data to understand trends and inform business decisions. Essentially, data science can be seen as the overarching field, while data analytics is a specific task within it.