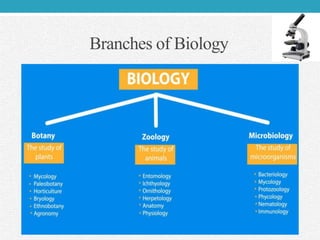
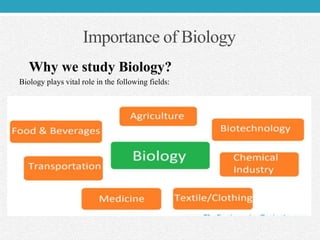
Biology is defined as the scientific study of living organisms, including their structure, function, behavior, and interactions with the environment. It has roots in ancient civilizations but developed into a modern science during the Renaissance. Key events included Darwin's theory of evolution by natural selection and the discovery of DNA's structure. Today, biology remains at the forefront of scientific discovery through fields like biotechnology, genomics, and synthetic biology.