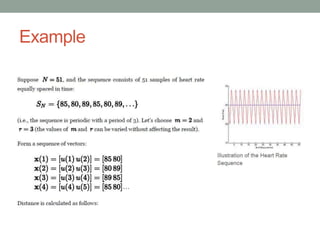
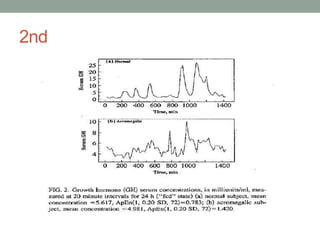
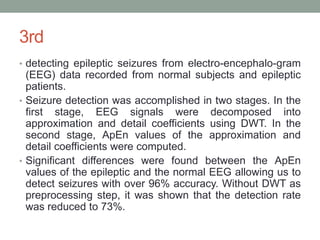
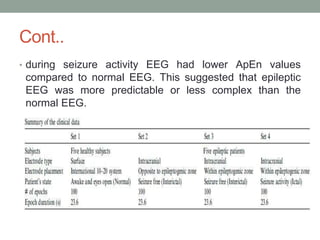
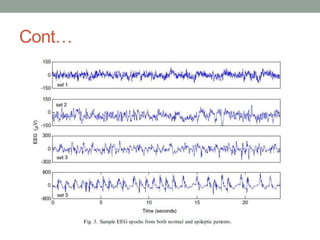
Approximate entropy (ApEn) is a technique used to quantify the unpredictability and regularity of fluctuations in time-series data. It reflects the likelihood that similar patterns will not be followed by additional similar observations. ApEn is useful for relatively short, noisy time-series data, as it is less affected by noise and has lower computational demands than other complexity measures. ApEn has been used to successfully distinguish patient groups in applications like endocrine hormone secretion and epilepsy detection from EEG data, with accuracies over 90% in some cases. It has advantages over entropy as it can be used on smaller sample sizes and applied in real-time applications.

![Introduction
• Developed by Steve M. Pincus
• an approximate entropy (ApEn) is a technique used to
quantify the amount of regularity and the unpredictability
of fluctuations over time-series data, which appears to
have potential application to a wide variety of relatively
short (range 50-5000) and noisy time-series data.
• motivated by data length constraints commonly
encountered, e.g., in heart rate, EEG, and endocrine
hormone secretion data sets.
• Findings have discriminated groups of subjects via ApEn,
in instances where classical [mean, standard deviation
(SD)] statistics did not show clear group distinctions](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/approximateentropy-180908085833/85/Introduction-to-Approximate-entropy-3-320.jpg)