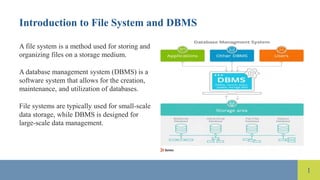
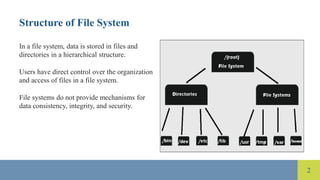
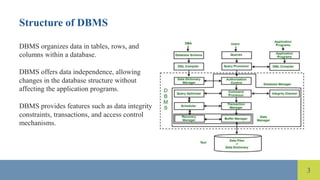
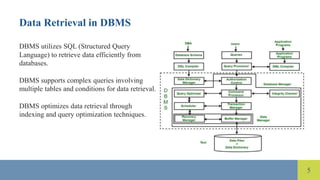
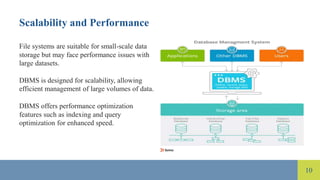
The document compares file systems and database management systems (DBMS), highlighting that file systems are suitable for small-scale storage with direct user control, while DBMS are designed for large-scale data management with features like data integrity and security. DBMS utilizes SQL for efficient data retrieval and reduces data redundancy through normalization, whereas file systems often lead to redundancy and inconsistencies. Additionally, DBMS provides advanced security measures compared to limited security in traditional file systems.