Python is a high-level, general-purpose programming language designed with an emphasis on readability, simplicity, and flexibility. Created by Guido van Rossum and released in 1991, Python has become one of the most popular programming languages in the world. It is widely used across a variety of domains, such as web development, data science, machine learning, artificial intelligence, automation, and scientific computing. This article will provide a comprehensive introduction to Python, its features, ecosystem, and practical applications, aimed at giving a detailed understanding of the language.
A Brief History of Python
Python was first conceived in the late 1980s as a successor to the ABC programming language, which was itself designed for teaching and simplicity. Guido van Rossum, a Dutch programmer, began work on Python in December 1989 at the Centrum Wiskunde & Informatica (CWI) in the Netherlands. Python’s main design goals were to be simple, readable, and allow for rapid development, while also supporting advanced features like object-oriented programming (OOP).
The first public version, Python 0.9.0, was released in February 1991. It was built with key features such as exception handling, functions, and modules, which were critical for supporting large-scale applications. The language has evolved significantly over the years, with major milestones in Python 2.x and Python 3.x.
Python 2.x (released in 2000) became widely used for many years, but it reached its end of life in January 2020. Since then, Python 3.x has become the standard, offering improved syntax, new features, and better performance. The transition from Python 2 to Python 3 was not backward compatible, which led to a gradual migration by the Python community.
Key Features of Python
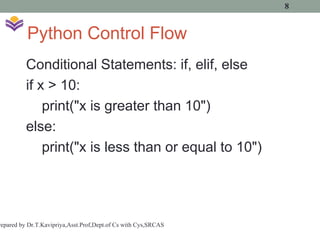
1. Readable and Simple Syntax
One of Python’s most distinguishing features is its simple and readable syntax. Python was designed to be as intuitive as possible, even for non-programmers, making it an ideal language for beginners. It avoids unnecessary syntax and uses clear, English-like keywords. Python code tends to be shorter and more readable compared to other languages like C++, Java, or Perl.
For example, in Python, indentation is used to define code blocks, rather than curly braces or semicolons, making the code more structured and visually appealing. This enforces good coding practices and ensures that Python code remains easy to follow.
Example:
python
Copy
if x > 10:
print("x is greater than 10")
else:
print("x is less than or equal to 10")
2. Dynamically Typed
Python is a dynamically typed language, which means that you don’t need to explicitly declare the type of a variable when you create it. The interpreter determines the type of the variable at runtime based on the assigned value. This makes Python code more concise and flexible, as the programmer doesn’t need to worry about type annotations.
For example:
python
Copy
x = 5 # x is an integer
x = "hello" # x is




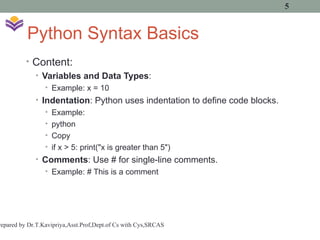
![Python Data Types
• Integers: x = 5
• Floats: y = 3.14
• Strings: name = "Python"
• Lists: numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4]
• Dictionaries: student = {"name": "John",
"age": 21}
6
repared by Dr.T.Kavipriya,Asst.Prof,Dept.of Cs with Cys,SRCAS](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductionaboutpython-250405074655-4fd87df8/85/Introduction-about-python-programming-ppt-6-320.jpg)