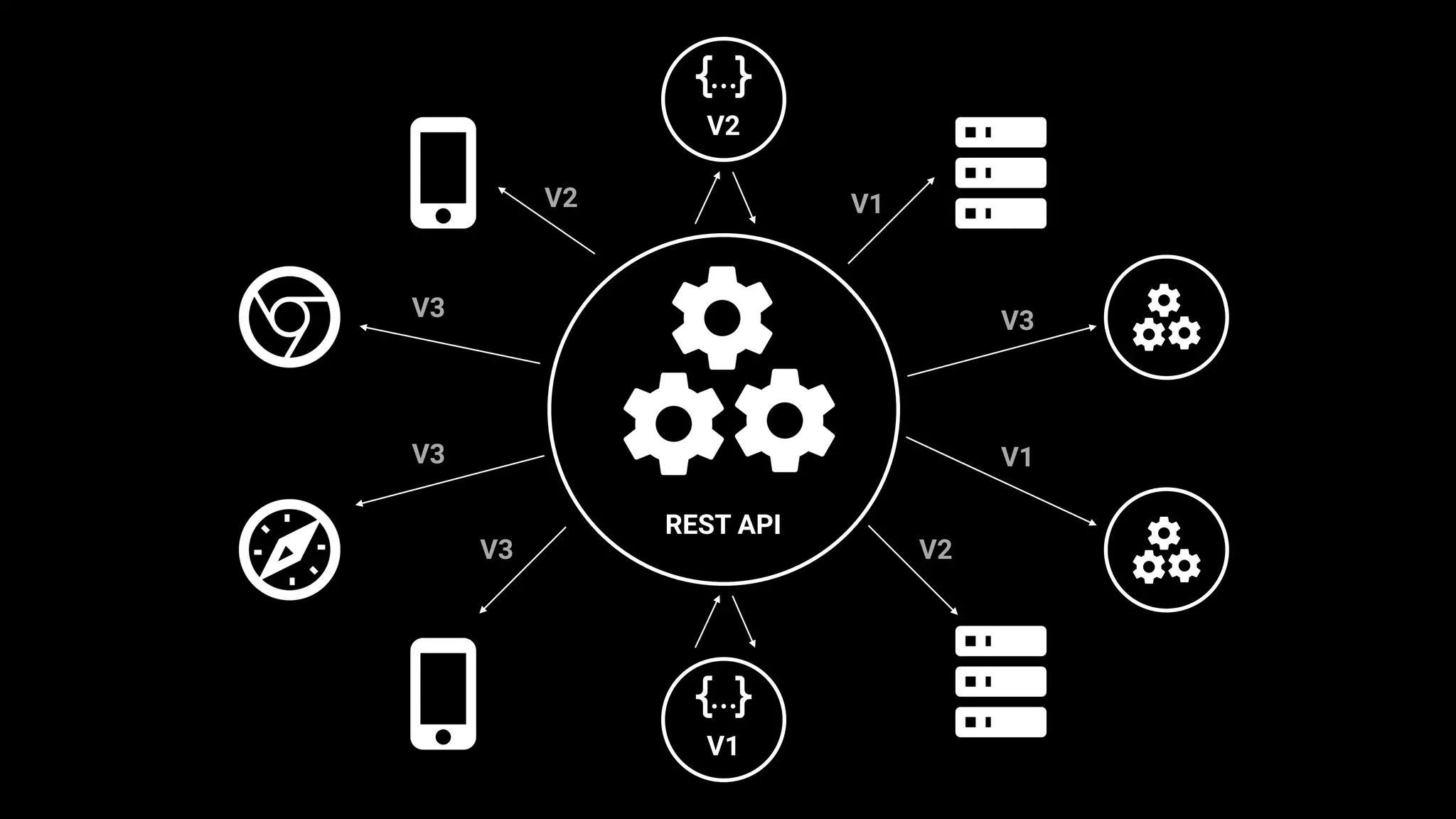
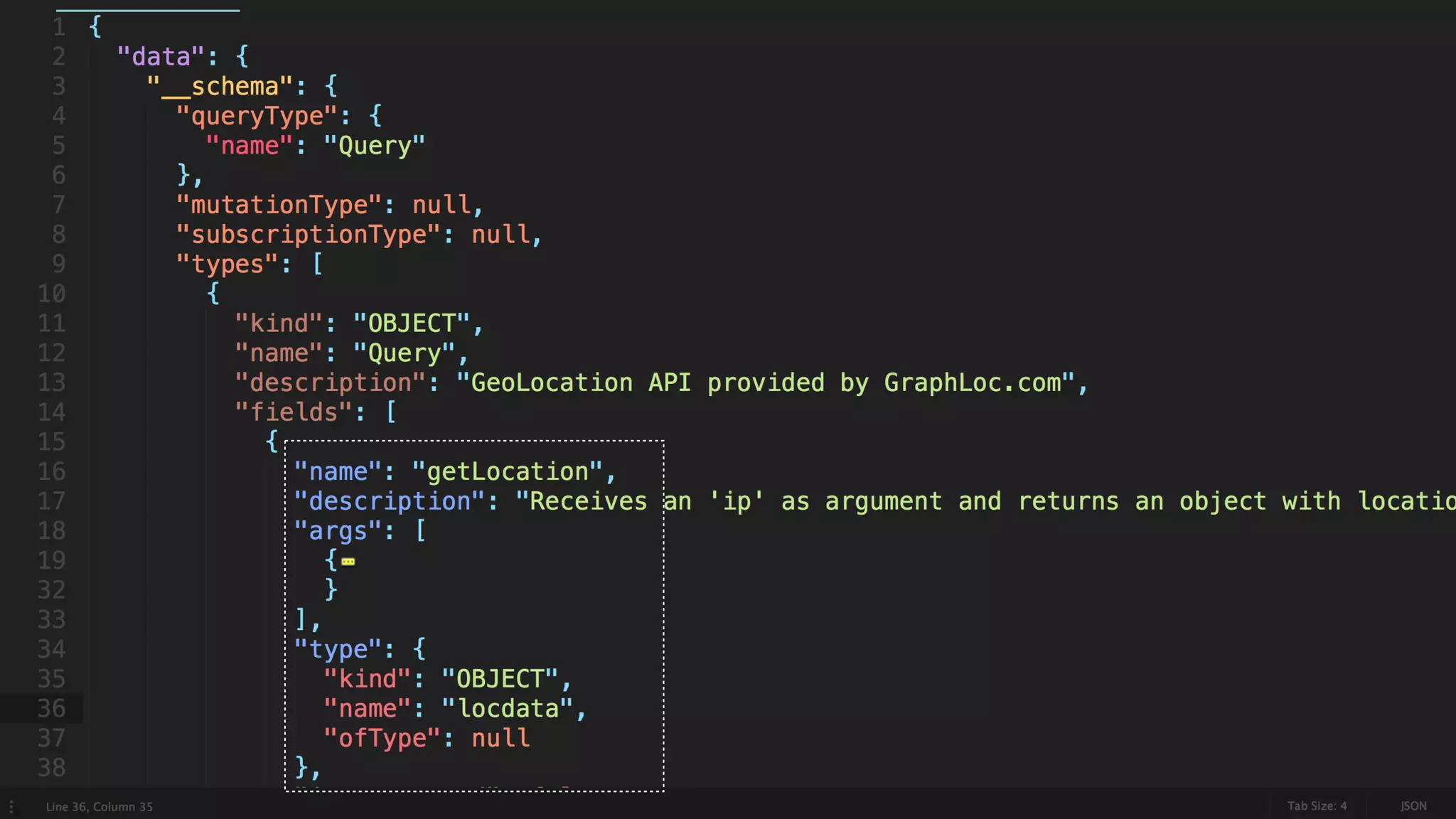
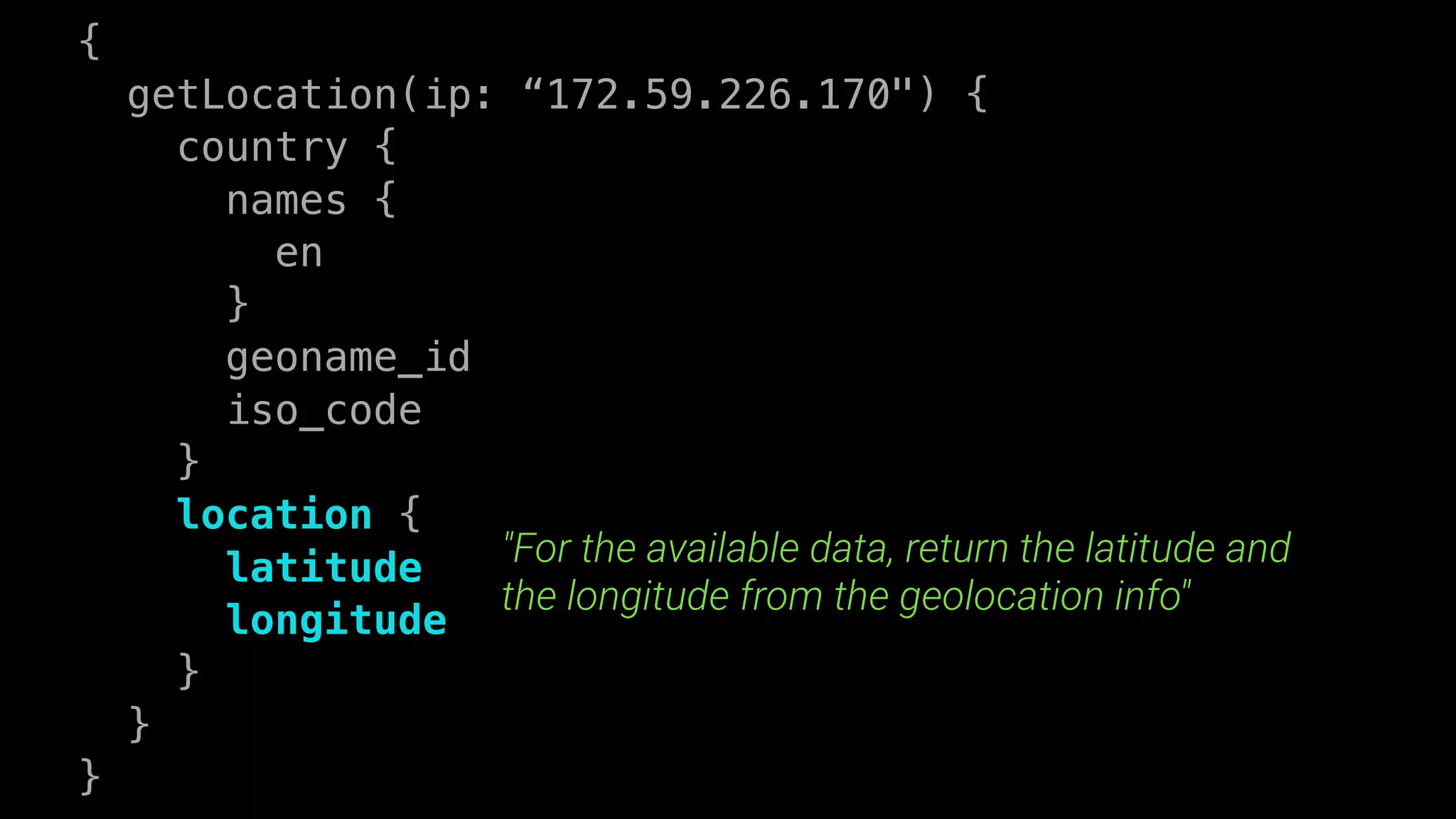
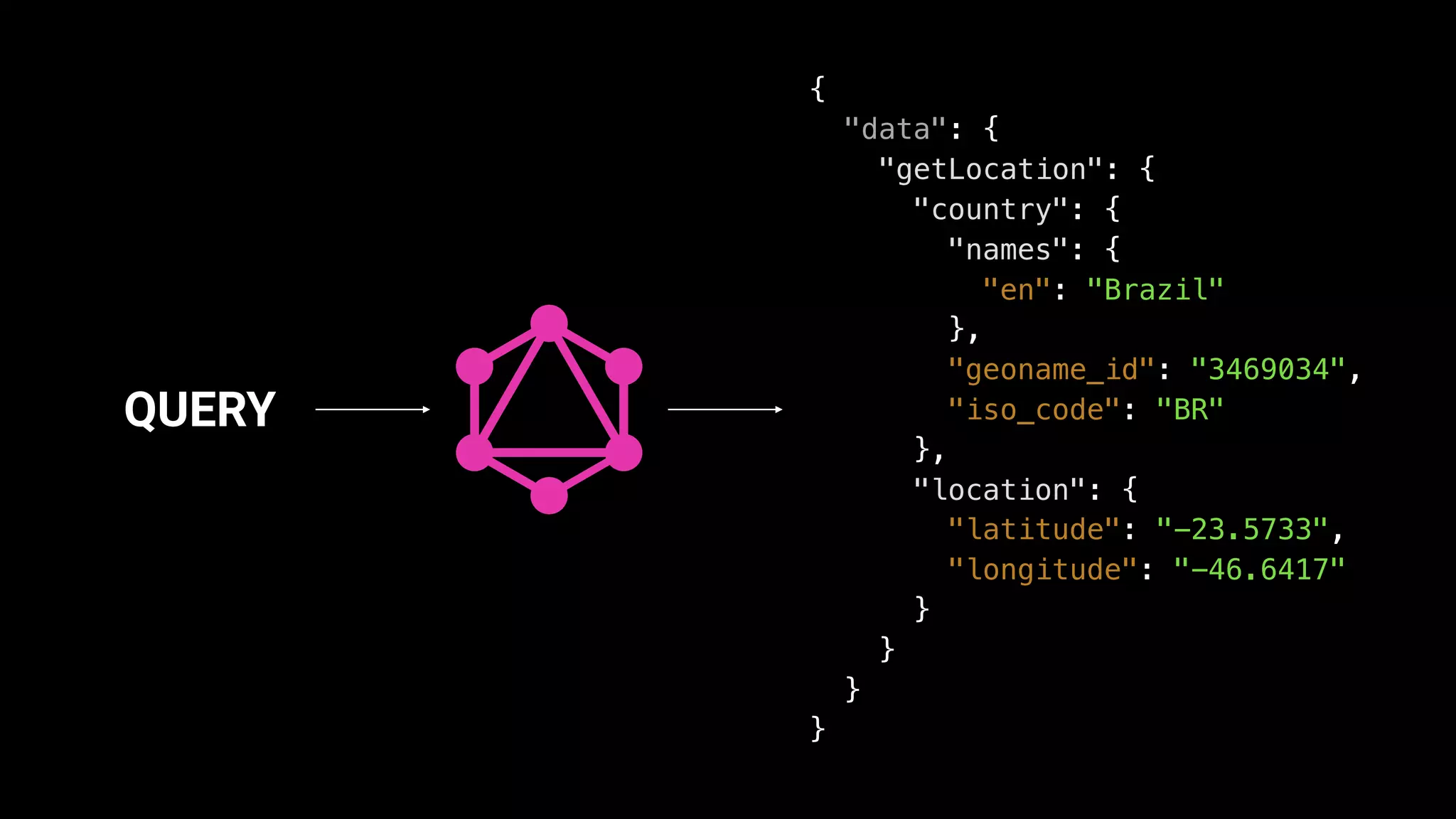
This document discusses GraphQL and how it compares to REST APIs. It outlines some common issues with REST APIs like versioning headaches and making multiple requests to fetch needed data. The core concepts of GraphQL are then explained, including how it uses a single endpoint and schema to define the data contract. Queries and mutations are covered as the main operations in GraphQL along with its type system. Potential concerns about using GraphQL for businesses are addressed at the end.