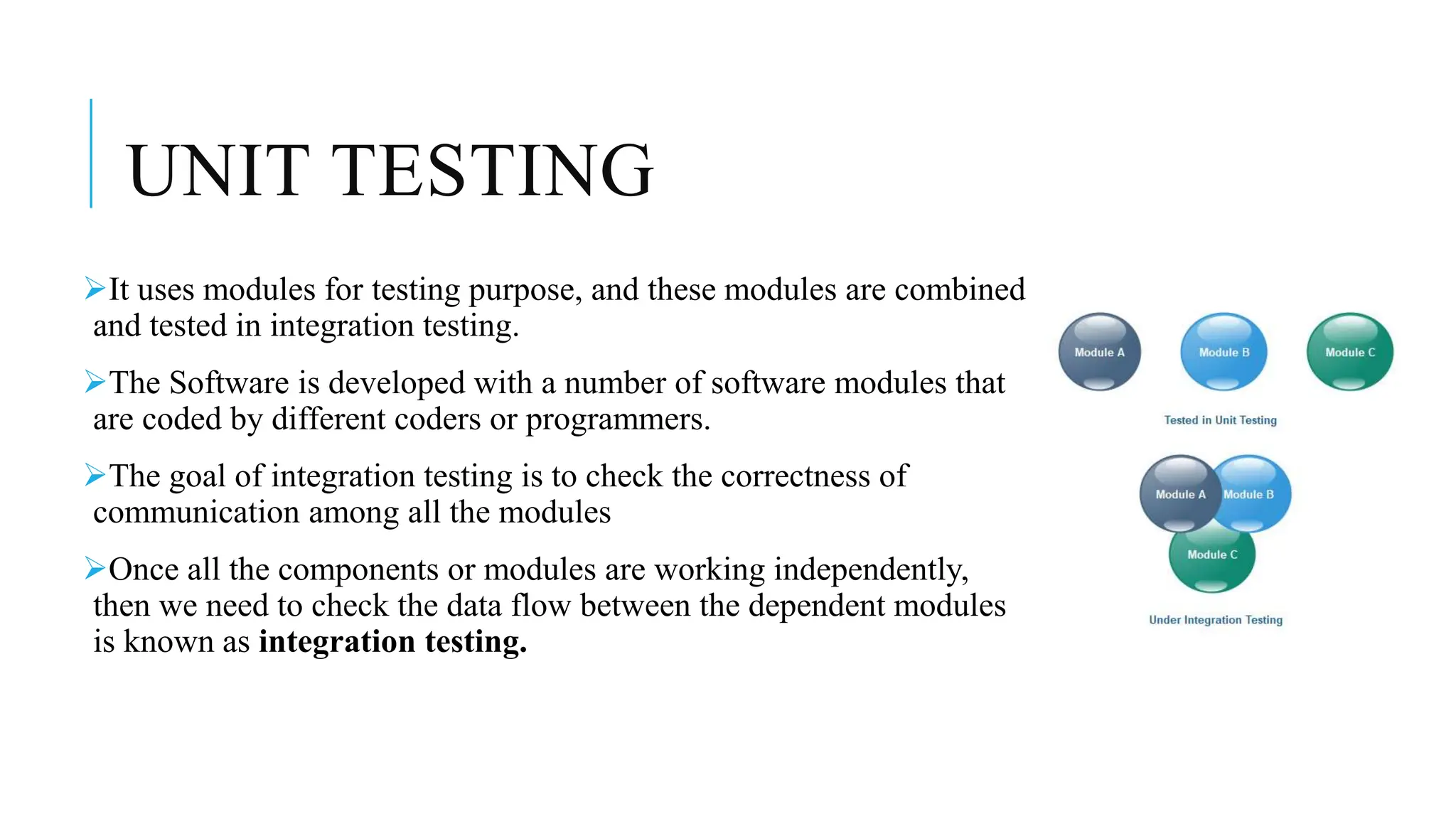
Integration testing is a crucial process for validating the interactions between software modules, primarily aiming to identify interface faults. It includes various types such as incremental, big bang, top-down, and bottom-up approaches and plays a vital role in enhancing system reliability, albeit with complexity and cost challenges. A case study on a social media platform, 'connect me', illustrates the importance of integration testing in ensuring a seamless user experience and reliable third-party integrations.