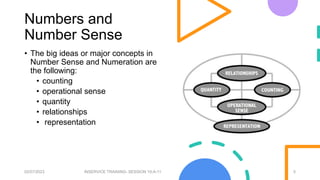
This document outlines an agenda and materials for a teacher training on number sense, place value, and basic operations. Session 10A covers number sense, counting strategies, and the key concepts of counting. Session 10B discusses place value, the decimal system, and strategies for teaching these concepts using manipulatives and the concrete-pictorial-abstract approach. Session 11 focuses on multi-digit addition and subtraction, with an emphasis on developing students' operational sense through problem-solving contexts.