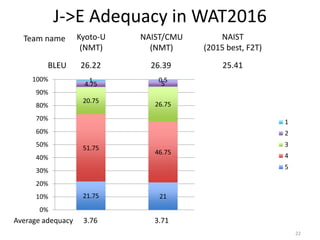
The document presents a model for selecting insertion positions for flexible non-terminals in dependency tree-to-tree machine translation, developed by Toshiaki Nakazawa and colleagues. The model aims to reduce the number of insertion positions, thereby enhancing translation quality and decoding speed. Experimental results show improved accuracy and BLEU scores when using the proposed model compared to traditional methods.

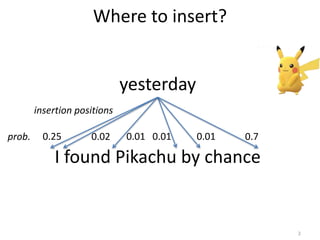
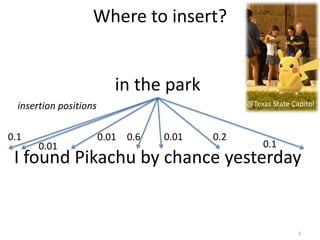
![Pikachu
Dependency Tree-to-Tree Translation
私
は
昨日
公園
で
ピカチュウ
を
見つけた
私
は
を
見つけた
I
found
by
Input Translation Rules Output
ピカチュウ Pikachu
偶然
[X7]
[X7]
偶然
chance
I
found
by
[X7]
chance
公園 the
park
昨日 yesterday
で 4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/emnlp2016-161110040336/85/Insertion-Position-Selection-Model-for-Flexible-Non-Terminals-in-Dependency-Tree-to-Tree-4-320.jpg)
![Dependency Tree-to-Tree Translation
私
は
昨日
公園
で
ピカチュウ
を
見つけた
私
は
を
見つけた
Input Translation Rules Output
ピカチュウ Pikachu
偶然
公園 the
park
[X7]
偶然
昨日 yesterday
で
[X]
[X]
[X]
[X]
found
by
chance
[X]
I
[X7]
found
Pikachu
by
I
chance
yesterday
the
park
in
found
Pikachu
by
I
chance
yesterday
Pikachu
I
found
by
chance
Flexible Non-terminals
[Richardson+, 2016]
floating
subtree
floating
subtree
5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/emnlp2016-161110040336/85/Insertion-Position-Selection-Model-for-Flexible-Non-Terminals-in-Dependency-Tree-to-Tree-5-320.jpg)
![Appropriate Insertion Position Selection
• roughly half of all translation rules were
augmented with flexible non-terminals
[Richardson+, 2016]
• flexible non-terminals make the search space
much bigger -> slower decoding speed,
increased search error
• reduce the number of possible insertion
positions in translation rules by a Neural
Network model
7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/emnlp2016-161110040336/85/Insertion-Position-Selection-Model-for-Flexible-Non-Terminals-in-Dependency-Tree-to-Tree-7-320.jpg)
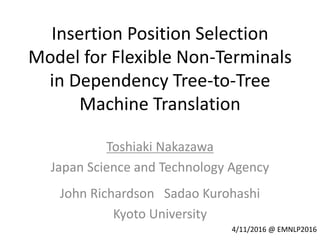


![Information for Selection Model
私
は
昨日
公園
で
ピカチュウ
を
見つけた
私
は
を
見つけた
Input Translation Rules
偶然
[X7]
偶然
found
by
chance
I
[X7]
I
Ps
Pt
Sp
Sn
Ds
=
4
[X]
Dt
=
-2
Non-terminals:
reverted to the
original word in
the parallel
corpus
11
[yesterday]
[found]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/emnlp2016-161110040336/85/Insertion-Position-Selection-Model-for-Flexible-Non-Terminals-in-Dependency-Tree-to-Tree-11-320.jpg)
![Information for Selection Model
私
は
昨日
公園
で
ピカチュウ
を
見つけた
私
は
を
見つけた
Input Translation Rules
偶然
[X7]
偶然
found
by
chance
I
[X7]
I
Ps
Pt
Sp
Sn
Ds
=
4
[X]
Dt
=
-3
= [POST-BOTTOM]
12
[yesterday]
[found]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/emnlp2016-161110040336/85/Insertion-Position-Selection-Model-for-Flexible-Non-Terminals-in-Dependency-Tree-to-Tree-12-320.jpg)
![Training Data Creation
• Training data for the NN model can be
automatically created from the word-aligned
parallel corpus
– consider each alignment as the floating word and
remove it from the target tree
14
私
は
を
見つけた
I
found
by
ピカチュウ
Pikachu
偶然
chance
[X]
[X]
[X]
[X]
label
0
0
0
1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/emnlp2016-161110040336/85/Insertion-Position-Selection-Model-for-Flexible-Non-Terminals-in-Dependency-Tree-to-Tree-14-320.jpg)

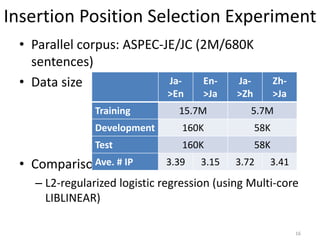
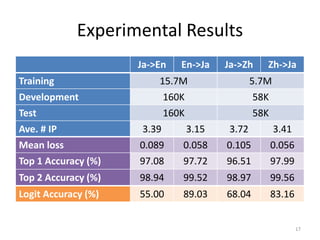
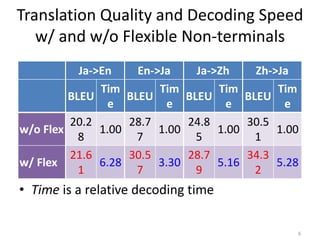
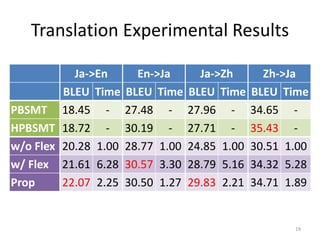
![Translation Experiment
• Parallel corpus: ASPEC-JE/JC (2M/680K
sentences)
• Decoder: KyotoEBMT [Richardson+, 2014]
• 5 Settings
– Phrase-based and hierarchical phrase-based SMTs
– w/o Flex: not using flexible non-terminals
– w/ Flex: baseline with flexible non-terminals
– Prop: using insertion position selection (only top 1)
• BLEU and relative decoding time
18](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/emnlp2016-161110040336/85/Insertion-Position-Selection-Model-for-Flexible-Non-Terminals-in-Dependency-Tree-to-Tree-18-320.jpg)

![Future Work
• Use grand-children’s info
– Recursive NN [Liu et al., 2015] or Convolutional
NN [Mou et al., 2015]
• Shift to NMT!!
– Actually, we’ve already shifted and participated
WAT2016 shared tasks
• However, NMT is still far from perfect
21](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/emnlp2016-161110040336/85/Insertion-Position-Selection-Model-for-Flexible-Non-Terminals-in-Dependency-Tree-to-Tree-21-320.jpg)