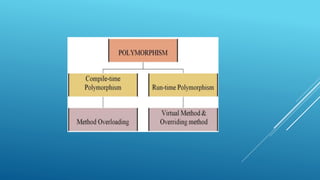
The document discusses inheritance in Java, detailing its definition, types, and significance for code reusability. It explains concepts such as single, multiple, multilevel, hierarchical inheritance, and method overriding, including example programs to illustrate each concept. Additionally, the document introduces polymorphism and the use of the 'super' keyword to reference parent class objects.


![Simple program
class super {
Public void display()
{
System.out.println(“I am parent class”);
}
}
class sub extends super {
public static void main(String args[])
{
sub message = new sub()
message.display();
}
}
Super
I am from parent class
sub
Parent class
Child classs
Output: I am parent class](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inheritance-240718023518-044bf823/85/Inheritance-single-multiple-access-rulepptx-5-320.jpg)


![SAMPLE PROGRAM OF SINGLE INHERITANCE :
class message_super {
Public void display()
{
System.out.println(“I am from superclass”);
}
}
class message_sub extends message_super {
public static void main(String args[])
{
Message_sub message = new message_sub()
Message.display();
}
}
Output: I am from superclass
message_super
I am from superclass
message_sub](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inheritance-240718023518-044bf823/85/Inheritance-single-multiple-access-rulepptx-8-320.jpg)
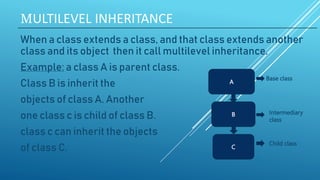
![SAMPLE PROGRAM OF MULTILEVEL INHERITANCE :
class a {
int data= 15; }
class b extends a {
}
class c extends b {
public void display() {
System.out.println(“number is:”+data);
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
c num= new c()
num.display();
}
}
Output: number is: 15
a
Data=15
b
c](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inheritance-240718023518-044bf823/85/Inheritance-single-multiple-access-rulepptx-10-320.jpg)


![Sample program of method overriding:
class animal {
public void display() {
System.out.println(“I am animal”); }
}
class tiger extends animal {
public void display() {
System.out.println(“I am tiger”);
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
tiger t = new tiger();
t.display(); }
}
Output: I am tiger](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inheritance-240718023518-044bf823/85/Inheritance-single-multiple-access-rulepptx-14-320.jpg)





![EXAMPLE OF SUPER KEYWORD
class Employee {
float salary=10000;
}
class HR extends Employee {
float salary=20000;
void display() {
System.out.println("Salary: "+super.salary);//print base class salary
}
}
class Supervarible {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HR obj=new HR();
obj.display();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inheritance-240718023518-044bf823/85/Inheritance-single-multiple-access-rulepptx-21-320.jpg)
