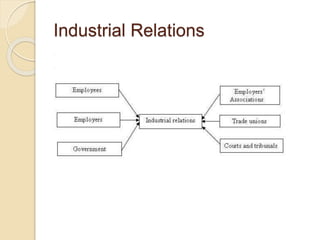
Industrial relations involves the relationship between employees and management, including interactions mediated by unions, employers, and the government. It encompasses collective bargaining, dispute resolution, worker participation, and regulation of unfair labor practices. Strong industrial relations are important for sustained production and worker satisfaction through high morale and reduced conflict. Trade unions also play an important role by representing workers, negotiating on their behalf, and providing economic security. Collective bargaining is a key process that establishes employment conditions through joint negotiation between company and union representatives.