1. The Industrial Experimental Plant is a facility that allows knowledge agents, enterprises, and technology developers to collaborate on developing new products, processes, and technologies for the natural and artificial stone sector.
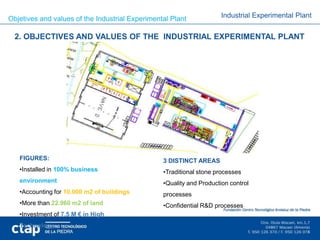
2. The plant has three technology areas - traditional stone processes, quality control processes, and confidential R&D processes. It aims to develop knowledge of stone transformation, train industry professionals, create collaboration spaces for enterprises, and transfer technologies to companies.
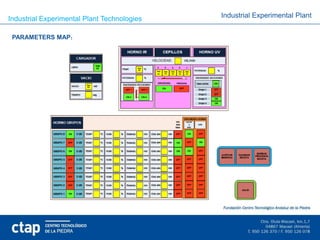
3. The plant has technologies for surface chemical treatment, mechanical treatment and texturing, stone block sawing, and composites formulation to further process and material development with a focus on parameter control and optimization. It has supported many successful collaborative projects.