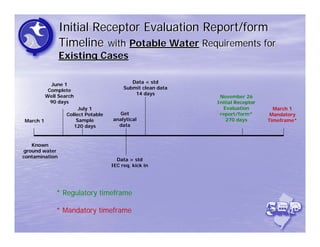
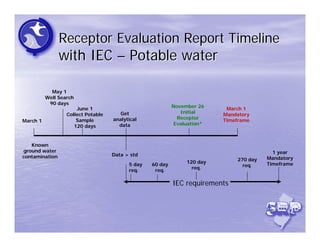
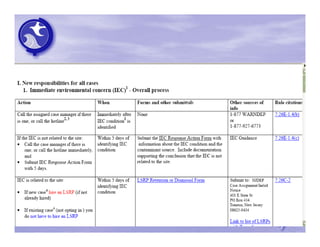
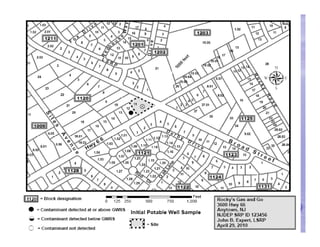
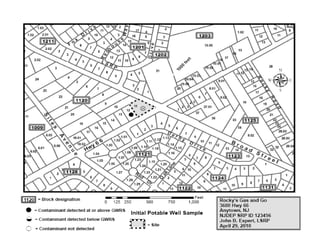
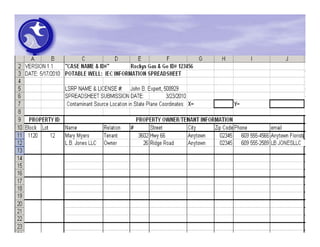
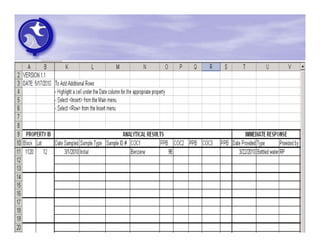
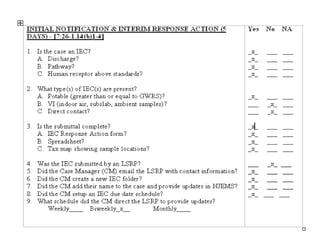
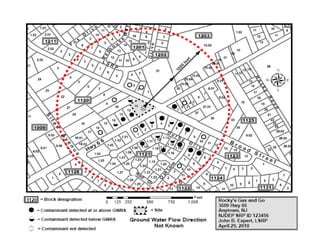
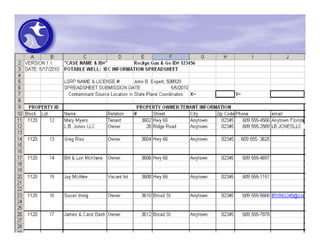
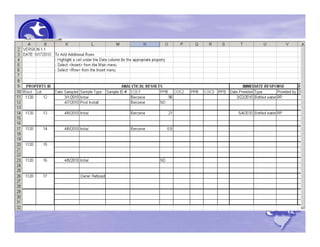
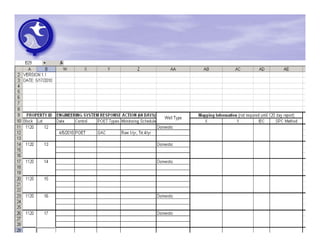
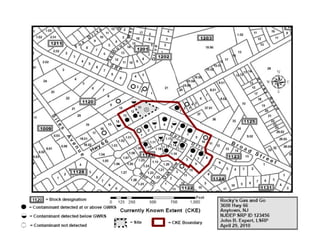
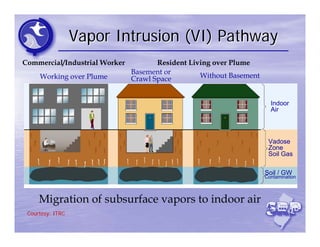
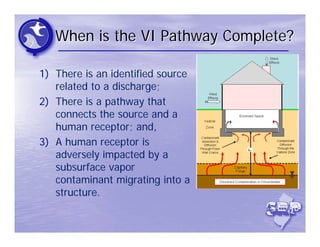
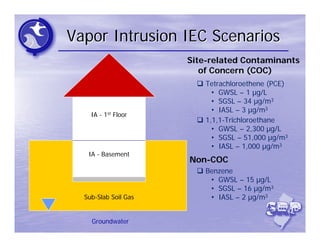
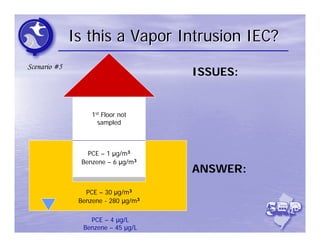
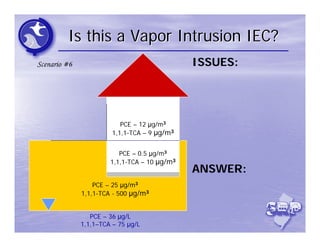
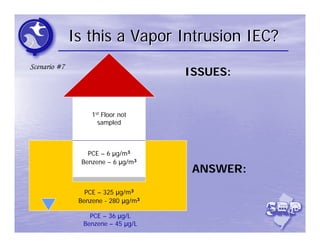
The document provides an overview of the Immediate Environmental Concern (IEC) process and tools used by the New Jersey Department of Environmental Protection. It discusses the regulatory timeframes for identifying and addressing IEC conditions, including notifying the department within 5 days, implementing mitigation within 60 days, and submitting an IEC source control report within 270 days. New quick reference guides have been developed to guide remediators through the IEC evaluation and reporting requirements. The presentation aims to explain the IEC tools and timeframes to facilitate compliance.