1) TEEB's origins stem from recognizing the economic significance of global biodiversity loss and the need to demonstrate biodiversity's value in economic terms.
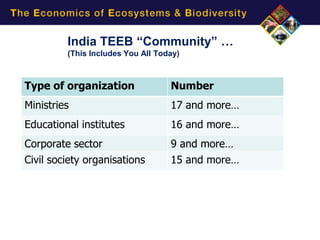
2) TEEB builds assets like reports, databases, and a collaborative community to advance its approach of recognizing, demonstrating and capturing ecosystems' value to support decision making.
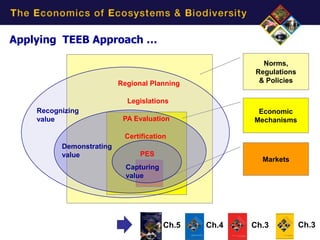
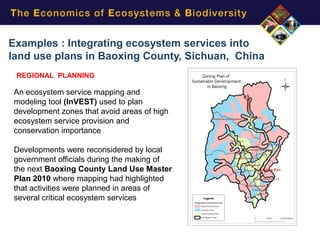
3) Examples show TEEB's approach applied through regional planning, legislation, protected area evaluation, certification, and payments for ecosystem services to integrate value into decisions and markets.







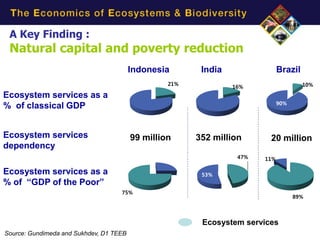
![A Key Recommendation :
Measuring better to manage better
Natural resources are economic assets, whether or not they enter the
marketpace
Conventional measures of national economic performance (eg : GDP
Growth) fail to reflect these stocks and their benefits flows.
Rapidly upgrade the System of National Accounts (SNA) to include
changes in natural capital stocks and ecosystem service flows
(CBD Strategic Plan – Target 2 ... in [..])
URGENT : physical accounts for forest stocks / carbon storage
need to be in place (e.g. for orderly development of REDD+)
Ch.3 Ch.3,5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/indiateeblaunch-pavansukhdev-110419020428-phpapp02/85/India-teeb-launch-pavan-sukhdev-11-320.jpg)