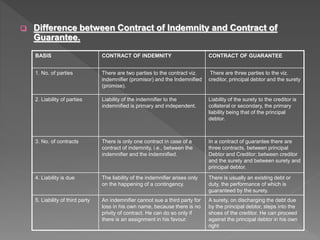
This document provides information about contracts of indemnity and guarantee under business law. It defines a contract of indemnity as one where one party promises to save the other from loss caused by the promisor or a third party. A contract of guarantee involves three parties where a surety promises to fulfill the liability of a principal debtor in case of default. The key differences between the two contracts are that indemnity involves two parties and primary liability, while guarantee involves three parties and secondary liability of the surety. The document outlines the rights and obligations of parties under these contracts.


![1. CONTRACT OF INDEMNITY
A contract by which one party promises to save the other from loss caused to
him by the conduct of the promisor himself, or by the conduct of any other
person, is called a ‘contract of indemnity. [section 124].
For Example - A contracts to indemnify B against the consequences of any
proceedings which C may take against B in respect of a certain sum of 200
rupees. This is a contract of indemnity.
PARTIES TO CONTRACT OF INDEMNITY:
INDEMNIFIER: The person who promises to indemnify.
INDEMNITY HOLDER: The person whose loss is to be indemnified.
Examples:
Motor insurance
Marine insurance
Fire insurance](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/indemnityandguarantee-220718164527-76c70a34/85/Indemnity_and_guarantee-pptx-3-320.jpg)

![2. CONTRACT OF GUARANTEE
A “contract of guarantee” is a contract to perform the promise, or discharge the liability, of a
third person in case of his default. A guarantee may be either oral or written. [section 126].
PARTIES TO CONTRACT OF GUARANTEE
SURETY: The person who gives the guarantee is called the “surety”. Person giving guarantee
is also called as ‘guarantor’. ;
PRINCIPAL DEBTOR: the person in respect of whose default the guarantee is given is called
the “principal debtor”, and
CREDITOR: the person to whom the guarantee is given is called the “creditor”.
Three parties are involved in contract of guarantee. Contract between any two of them is not
a ‘contract of guarantee’. It may be contract of indemnity.
Primary liability is of the principal debtor. Liability of surety is secondary and arises when
Principal Debtor fails to fulfill his commitments. However, this is so when surety gives
guarantee at the request of principal debtor. If the surety gives guarantee on his own, then it
will be contract of indemnity. In such case, surety has all primary liabilities.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/indemnityandguarantee-220718164527-76c70a34/85/Indemnity_and_guarantee-pptx-5-320.jpg)