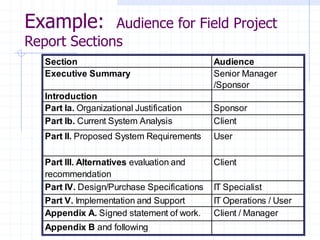
This document provides guidance on effective business communication and presentations. It outlines key components of presentations and reports, including defining the audience and purpose, using clear structure and formatting, presenting relevant data, stating conclusions, and emphasizing the importance and next steps ("So What?"). Effective presentations are concise, use visuals sparingly, and are well-rehearsed. The goal is for the audience to remember the main points and take appropriate action.