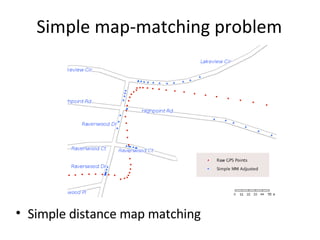
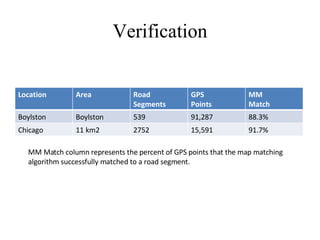
The document discusses improving the accuracy of wireless positioning systems using WiFi access points through a technique called look-ahead map-matching (LAMM). LAMM uses future GPS readings to help identify the current location on a digital map and constrain GPS readings to road segments. It presents three map-matching algorithms - simple distance based matching, map-matching with look-ahead, and look-ahead with smoothness constraint, and evaluates their ability to successfully match GPS points to road segments on test routes.