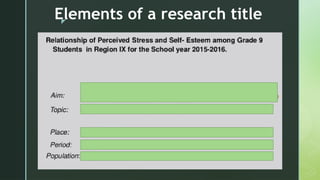
The document outlines the structure and key components of conducting qualitative and quantitative research, emphasizing the identification of research problems, topic selection, and research design. It details how to write effective research titles, criteria for selecting research topics, and suggests potential areas of investigation related to daily life. Additionally, it covers the significance of the research problem and offers guidance on narrowing down topics and formulating specific research questions.