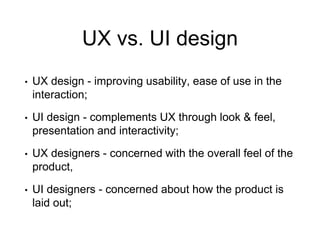
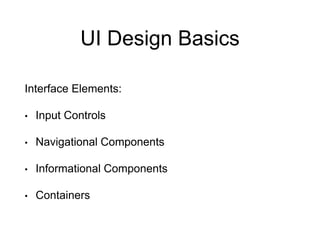
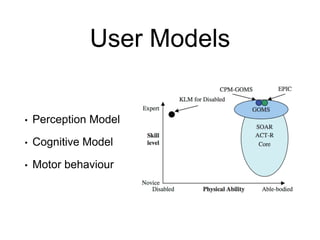
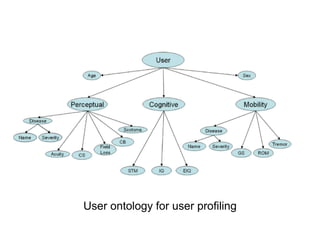
This document provides an overview of week 6 of the ICS3211 course on intelligent interfaces. It discusses visual design for user interfaces, including a recap of case studies, the differences between UX and UI design, best practices in UI design, evolutionary design principles, and designing for inclusive practices. The learning outcomes are also outlined.