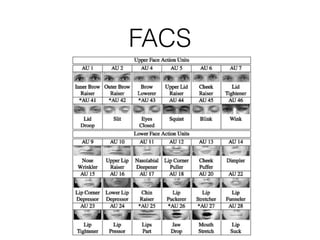
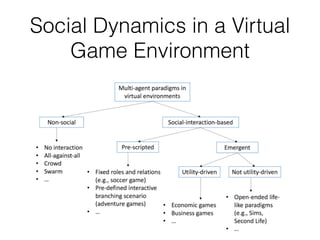
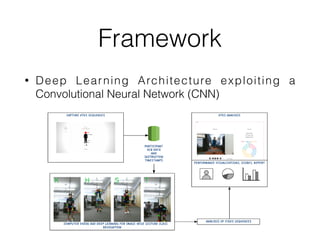
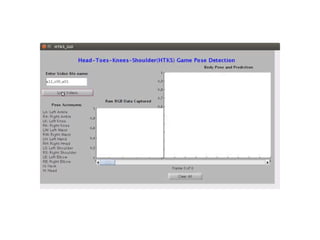
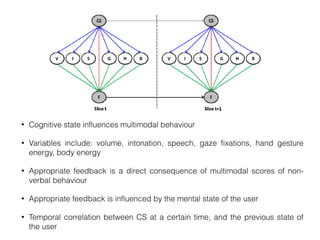
This document discusses topics related to emotion and cognition in smart systems, including emotional AI, emotion and cognition in games, and using machine learning and wearable devices to model cognitive behavior and intelligence. It describes several case studies, including using Microsoft Kinect to predict cognitive behavior by observing a game of Head-Shoulders-Knees-Toes, and using wearable devices and social signal processing to provide feedback to public speakers.