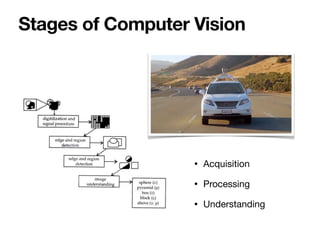
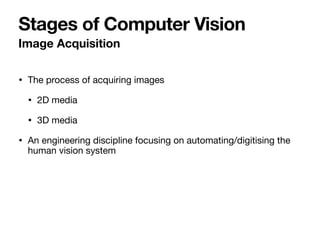
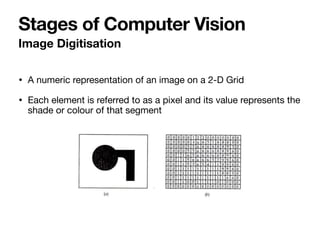
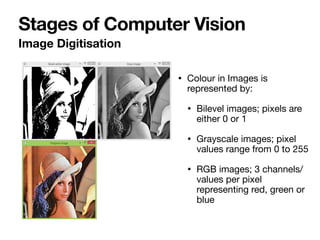
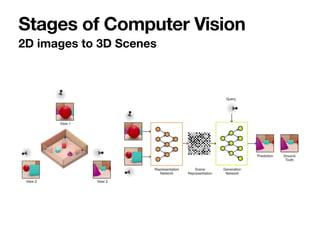
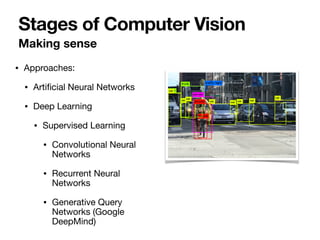
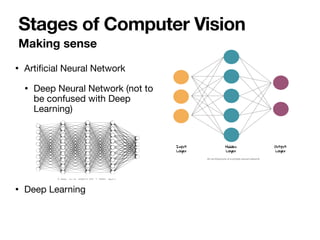
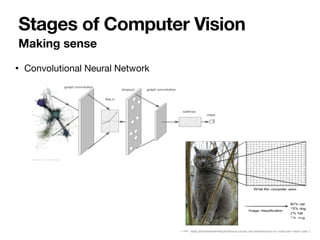
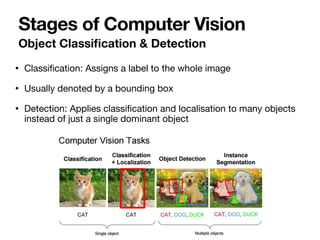
The document introduces Vanessa Camilleri, a lecturer in AI who is interested in computer vision, virtual reality, games, and machine learning education; it then provides an overview of computer vision, discussing how machines capture visual data through cameras, how images are digitized and represented, and the main techniques used to make sense of visual data including object detection, recognition and neural networks.