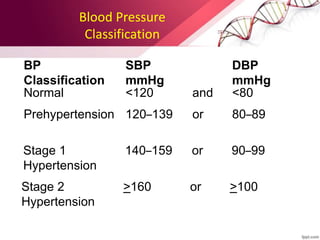
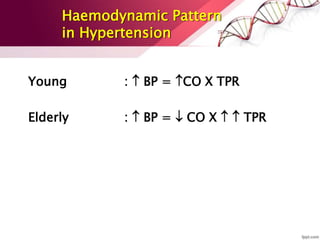
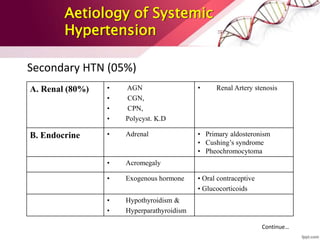
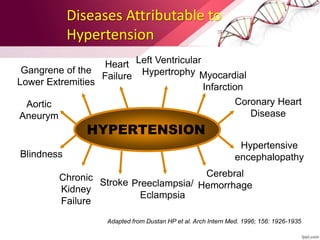
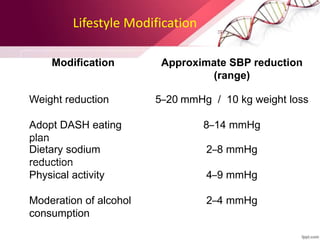
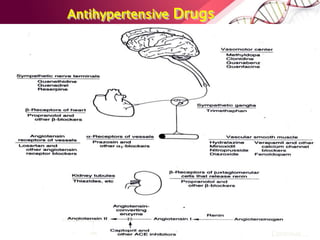
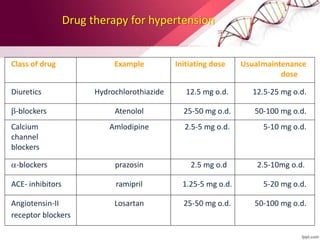
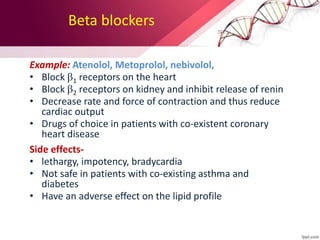
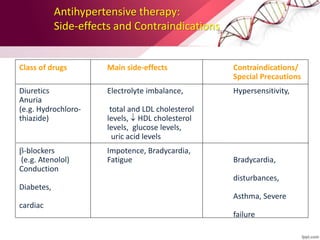
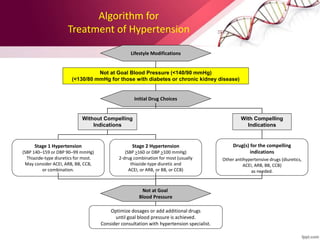
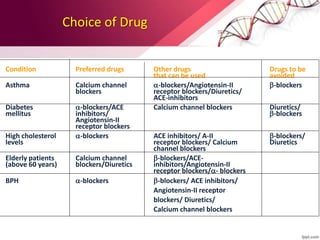
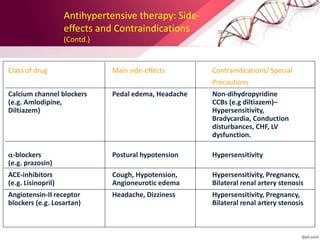
Hypertension is defined as blood pressure over 140/90 mmHg or taking medication for it. It can be essential or secondary hypertension. Treatment involves lifestyle modifications like weight loss, exercise, diet changes and medication if needed. Goals are to reduce blood pressure below 140/90 mmHg or 130/80 for those with diabetes or kidney disease. First line drugs include diuretics, ACE inhibitors, calcium channel blockers, and angiotensin receptor blockers. Multiple drugs may be needed and lifestyle changes are important to control hypertension.