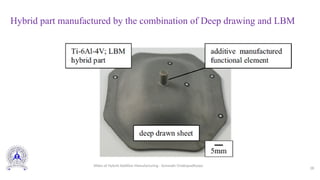
Hybrid additive manufacturing combines laser cladding with CNC operations in a single machine, allowing for precise metal deposition and machining along various axes. This technology enables the creation of complex geometries and materials not possible through traditional methods, potentially revolutionizing manufacturing processes. It integrates additive and subtractive techniques, improving part performance and versatility in design.




























![References
•[1] NX 11: Neue Entwicklungstechnologie für ein
neues Innovationszeitalter, www.siemens.com/plm
•[2] Slides of Ramesh Singh Machine Tools Lab,
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Indian
Institute of Technology Bombay
•[3] Marion Marklein et. al.,Friedrich-Alexander-
Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg, Egerlandstr. 13,
91058 Erlangen, Germany
33
Slides of Hybrid Additive Manufacturing - Somnath Chattopadhyaya](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hybridadditivemanufacturing-240919122621-0c06f776/85/Hybrid-Additive-Manufacturing-application-and-advanced-33-320.jpg)