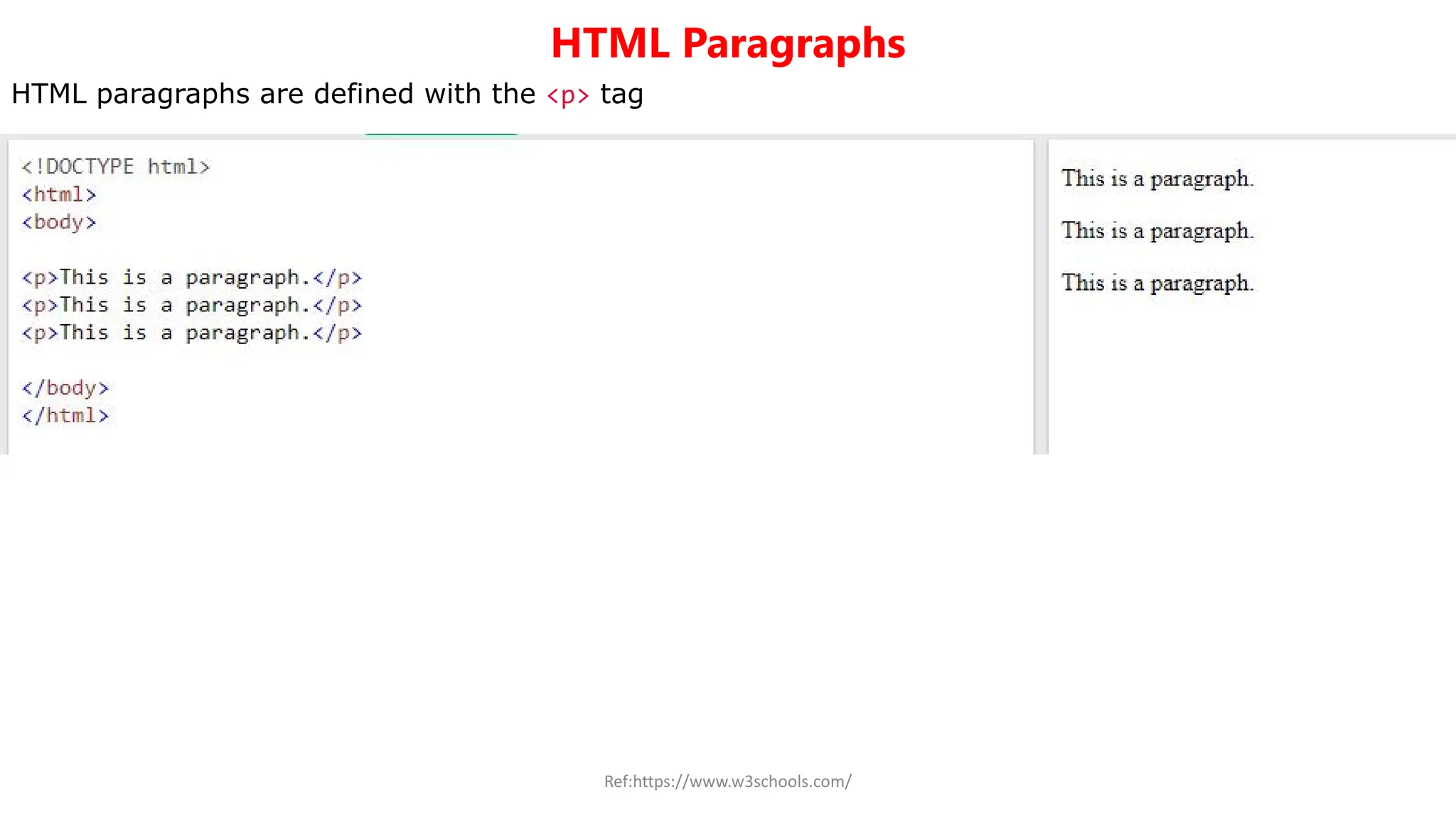
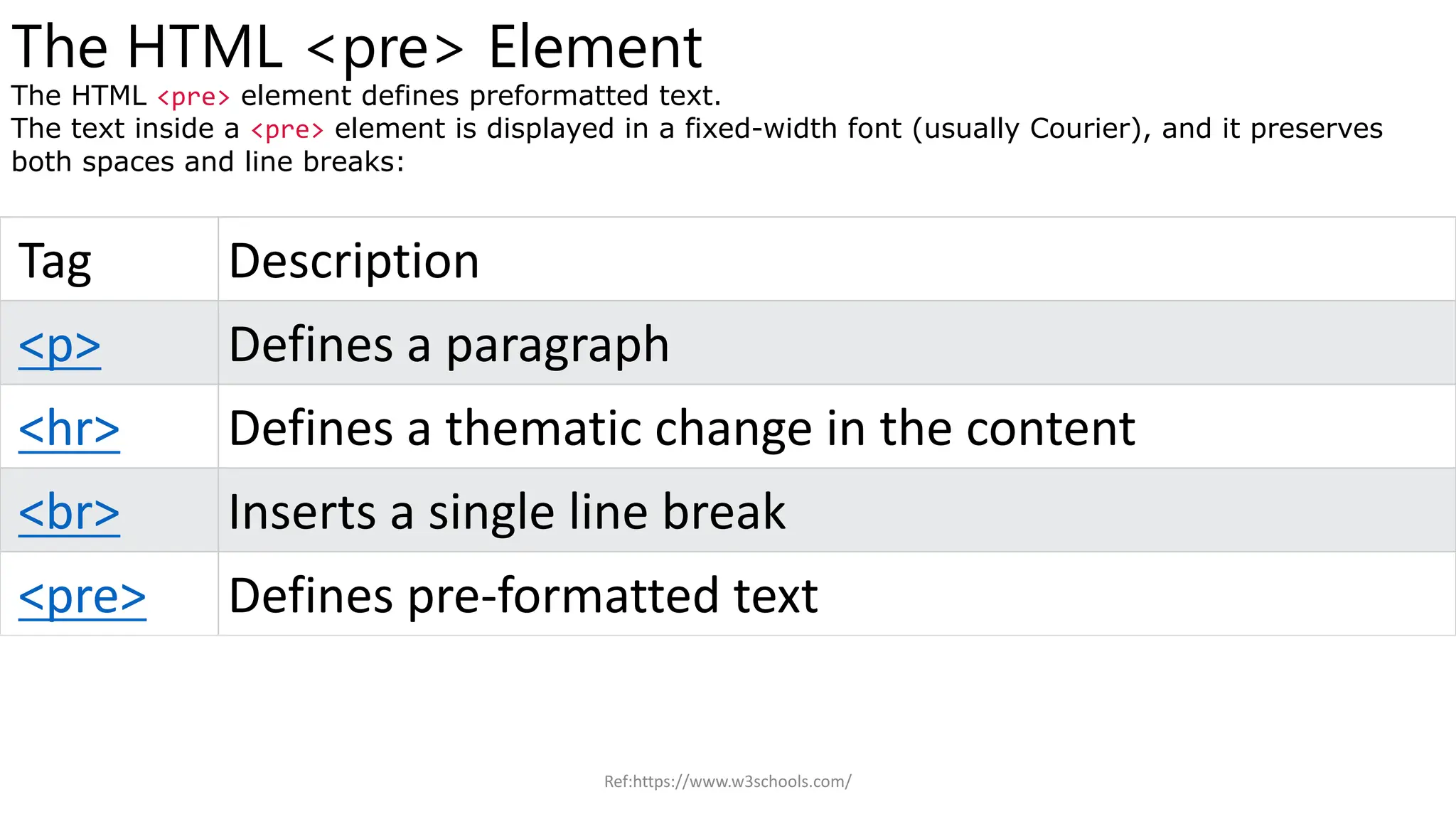
The document provides an overview of HTML (Hyper Text Markup Language), detailing its structure, elements, and usage for creating web pages. Key components include elements like <html>, <head>, <body>, and metadata specifications. It also describes basic tags such as headings, paragraphs, line breaks, and thematic breaks, along with their functions.