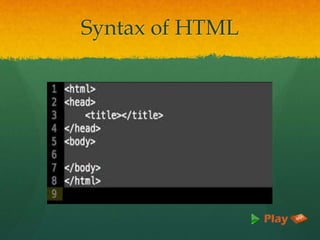
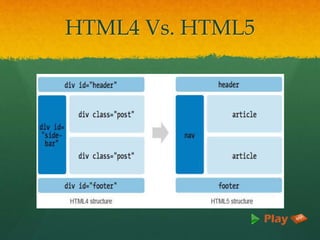
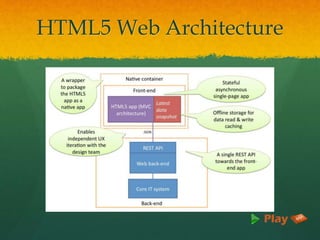
HTML (Hyper Text Markup Language) is the standard markup language for creating web pages, utilizing elements defined by tags. The document outlines the history, syntax, advantages, and evolution of HTML, including the transition from HTML4 to HTML5, which brings features like multimedia support and improved semantics. It emphasizes HTML's ease of use, wide browser support, and compatibility with XML.