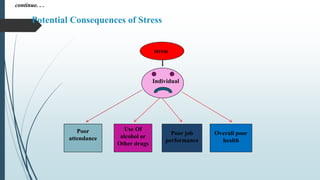
The document discusses employee safety, health, and wellness. It covers the role of HR professionals in promoting a safe work environment according to the Occupational Safety and Health Act of 1970. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) was created to ensure worker safety and health by working with employers and employees. OSHA requires employers to provide a safe workplace and protect employees from recognized hazards. The document also discusses wellness programs, stress, physical fitness programs, substance abuse, and employee assistance programs which organizations use to support employee health and deal with problems.