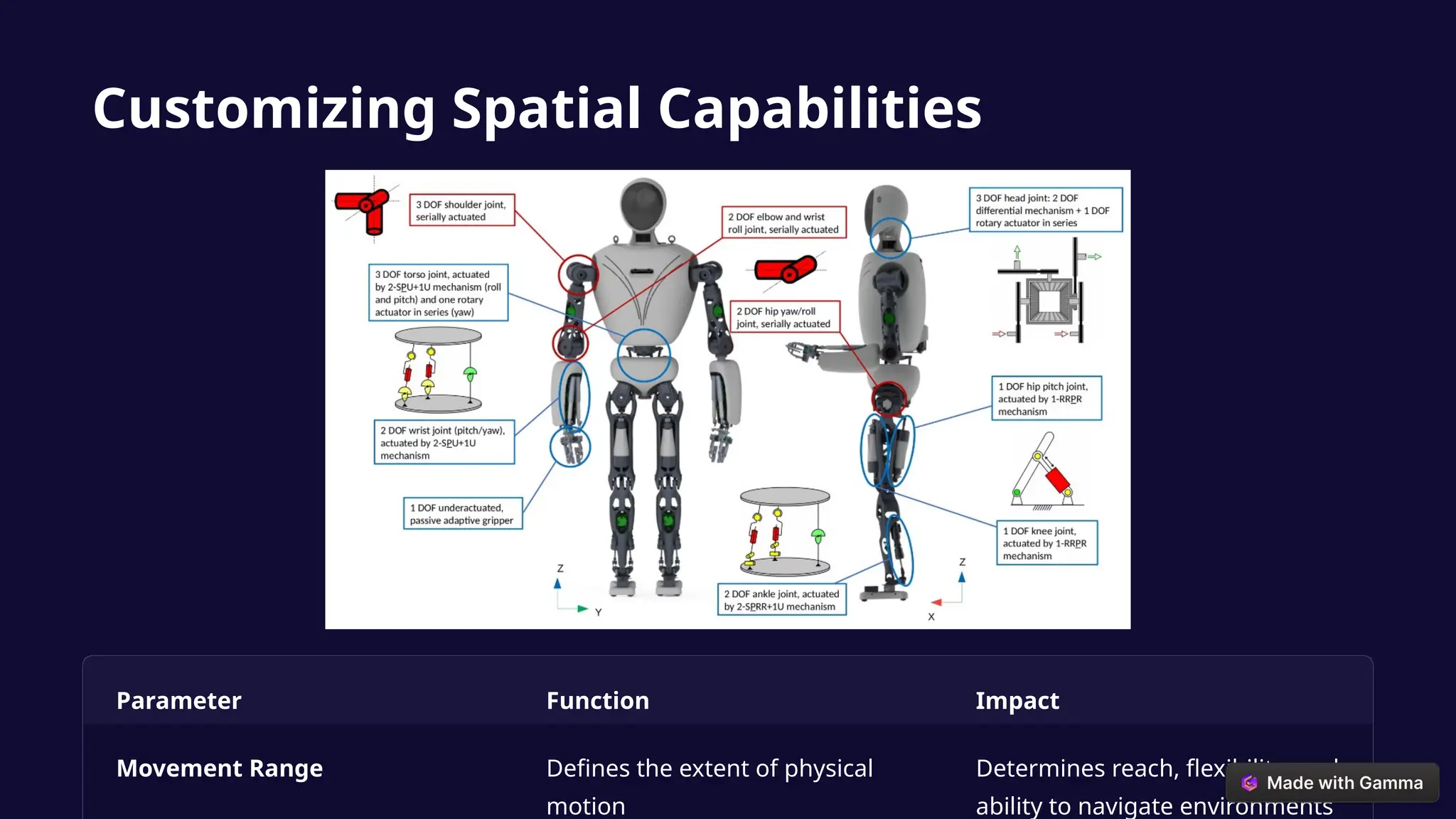
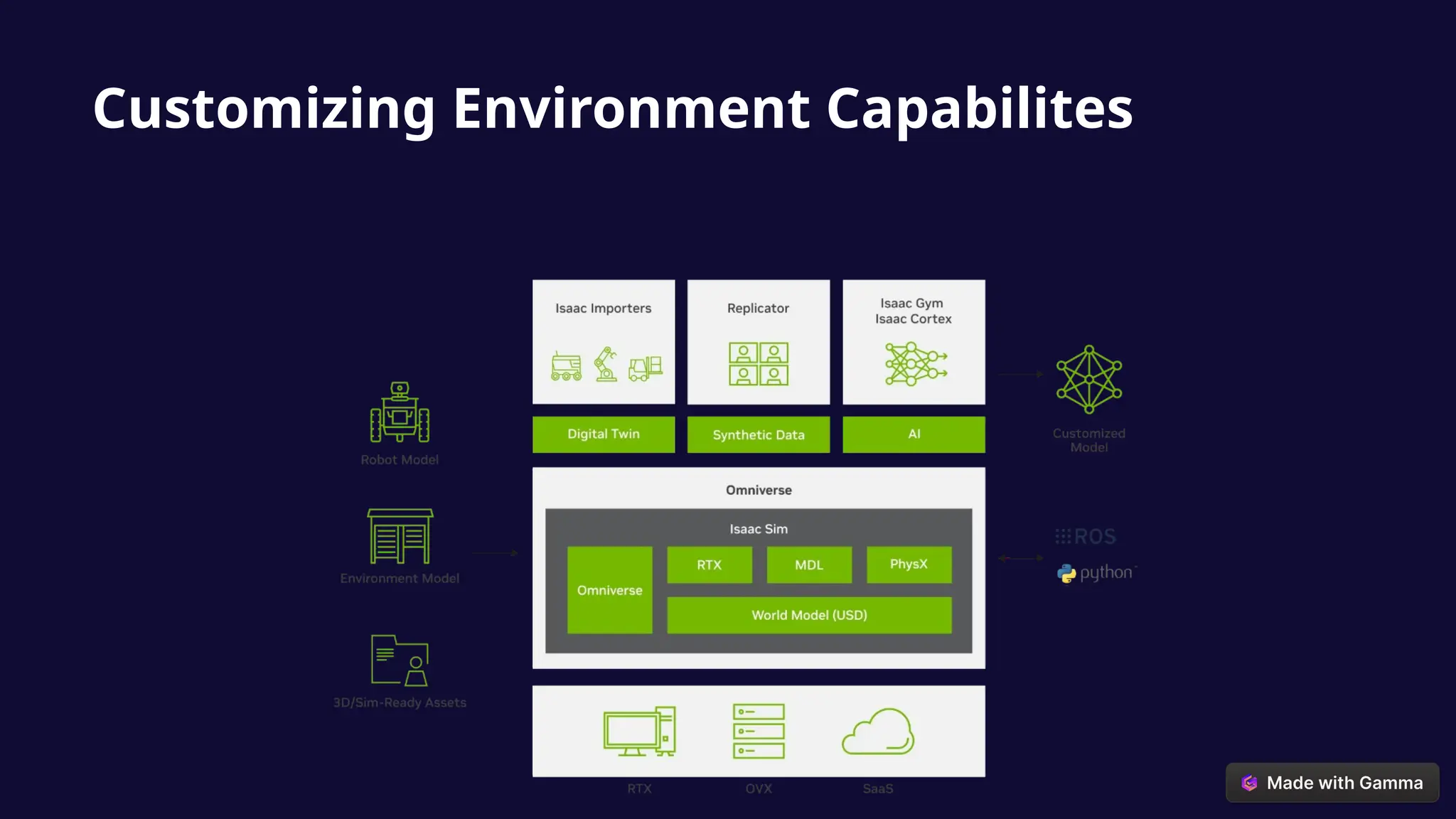
The document discusses the creation of artificial cognitive species through the convergence of AI, robotics, and digital environments, termed 'biocomputational speciation.' It outlines the processes of conceptualization, development, and operationalization, highlighting the advanced capabilities of synthetic brains and bodies that may challenge our definitions of life and consciousness. Additionally, it addresses the potential societal implications, including workforce transformation, redefined human relationships, ethical considerations, and alterations to social hierarchies.