The document outlines various methods to automate SEO projects using tools such as RStudio, Shiny Server, Jupyter Notebook, and Dataiku. It covers automation techniques for reporting, log analysis, keyword research, and semantic analysis, as well as the installation and usage of these tools. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of leveraging automation for SEO efficiency and adapting to advances in machine learning.






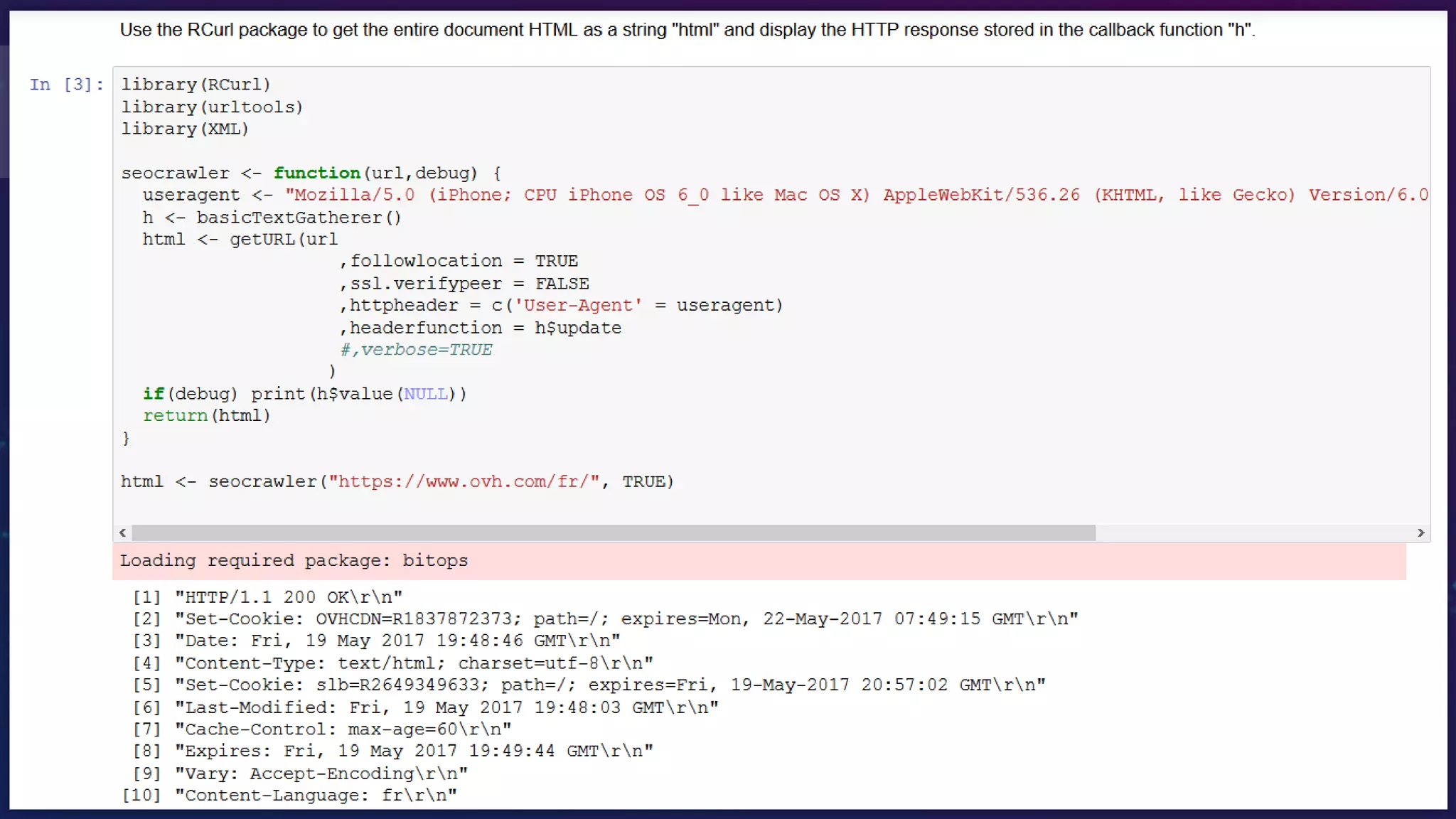
![R – Scraper – Header
ind0 <- grep("HTTP/",h$value(NULL))
df$StatusCode <- tail(h$value(NULL)[ind0],1)
ind1 <- grep("^Content-Type",h$value(NULL))
df$ContentType <- gsub("Content-Type:","",tail(h$value(NULL)[ind1],1))
ind2 <- grep("Last-Modified",h$value(NULL))
df$LastModified <- gsub("Last-Modified:","",tail(h$value(NULL)[ind2],1))
ind3 <- grep("Content-Language",h$value(NULL))
df$ContentLanguage <- gsub("Content-Language:","",tail(h$value(NULL)[ind3],1))
ind4 <- grep("Location",h$value(NULL))
df$Location <- gsub("Location:","",tail(h$value(NULL)[ind4],1))](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/conf-vps-r-shiny-teknseo-v19-170915190629/75/How-to-automate-all-your-SEO-projects-13-2048.jpg)
![R – Scraper – Xpath
doc <- htmlParse(html, asText=TRUE,encoding="UTF-8")
• H1 <- head(xpathSApply(doc, "//h1", xmlValue),1)
• H2 <- head(xpathSApply(doc, "//h2", xmlValue),1)
• robots <- head(xpathSApply(doc, '//meta[@name="robots"]', xmlGetAttr, 'content'),1)
• canonical <- head(xpathSApply(doc, '//link[@rel="canonical"]', xmlGetAttr, 'href'),1)
• DF_a <- xpathSApply(doc, "//a", xmlGetAttr, 'href')](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/conf-vps-r-shiny-teknseo-v19-170915190629/75/How-to-automate-all-your-SEO-projects-14-2048.jpg)


![R – Scraper – Test doMpi
library(doMPI)
#start your cluster
cl <- startMPIcluster(count=20)
registerDoMPI(cl)
#
max <- dim(mydataset)[1]
x <- foreach(i=1:max, .combine="rbind") %dopar% seocrawlerThread(mydataset,i)
#close your cluster
closeCluster(cl)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/conf-vps-r-shiny-teknseo-v19-170915190629/75/How-to-automate-all-your-SEO-projects-19-2048.jpg)



![R – Semantic Analysis – nGram
library(text2vec)
it <- itoken( DF_PotentialKeywords[['Keywords']],
preprocess_function = tolower,
tokenizer = word_tokenizer,
progessbar = F )
# 2 and 3 grams
vocab <- create_vocabulary(it, ngram = c(2L, 3L))
DF_SEO_vocab <- data.frame(vocab$vocab)
DF_SEO_select <- data.frame(word=DF_SEO_vocab$terms,
freq=DF_SEO_vocab$terms_counts) %>%
arrange(-freq) %>%
top_n(30)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/conf-vps-r-shiny-teknseo-v19-170915190629/75/How-to-automate-all-your-SEO-projects-25-2048.jpg)
















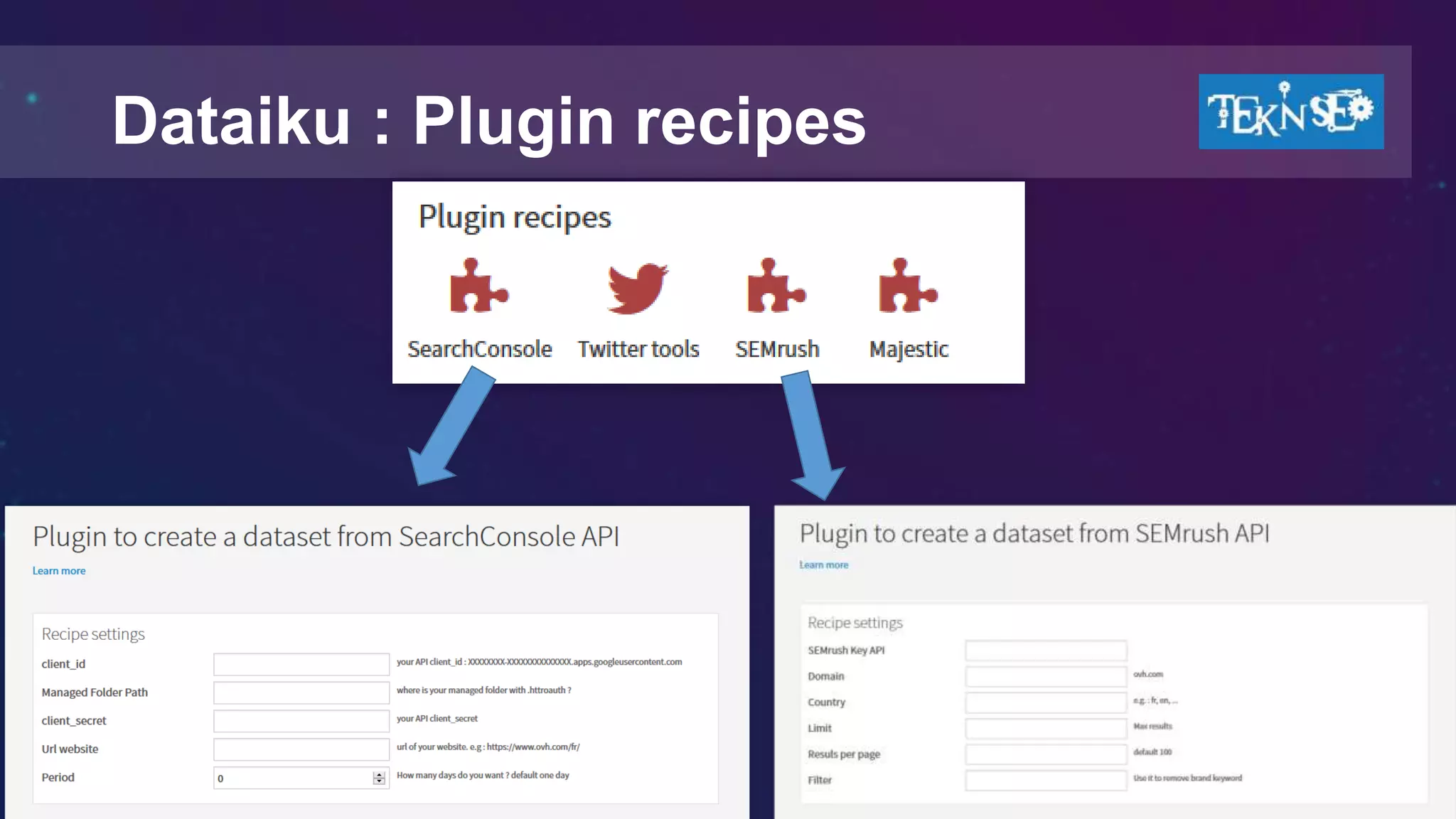
![Dataiku : My Plugins
• SEMrush
• SearchConsole
• Majestic
• Visiblis [ongoing]
A DSS plugin is a zip file.
Inside DSS, click the top right gear → Administration → Plugins → Store.
https://github.com/voltek62/Dataiku-SEO-Plugins](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/conf-vps-r-shiny-teknseo-v19-170915190629/75/How-to-automate-all-your-SEO-projects-64-2048.jpg)