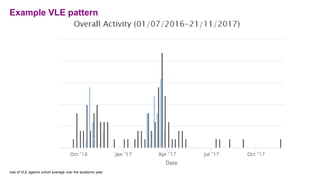
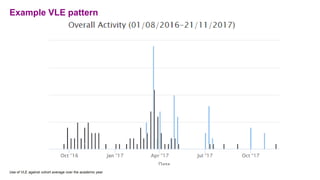
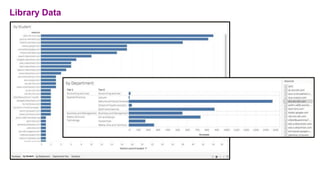
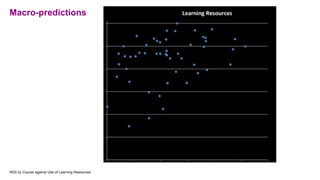
The document discusses how learning analytics can enhance the digital strategy at institutions like the University of Greenwich and the University of Gloucestershire, aiming to improve student engagement, retention, and learning experiences. It outlines their current tasks, data sources, analytics tools, and challenges related to implementing predictive models and governance practices. Furthermore, it emphasizes the importance of staff and student engagement, communication strategies, and utilizing data effectively for continuous improvement.