Embed presentation
Download to read offline





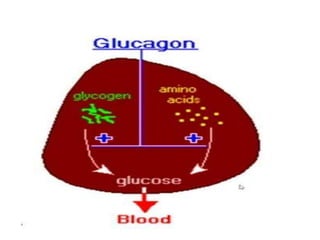


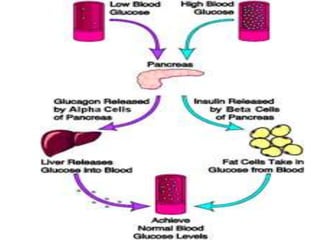
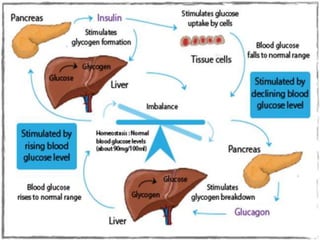


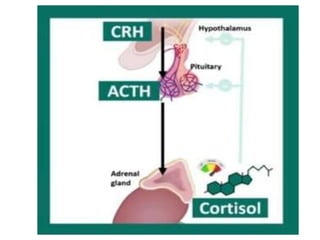

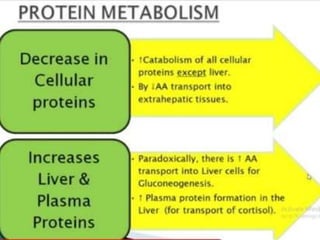

Glucagon is a 29 amino acid hormone secreted by the pancreas that functions opposite to insulin, being released when blood glucose levels fall to stimulate the liver to break down glycogen into glucose and increase gluconeogenesis from other substrates to raise blood sugar. Cortisol is a steroid hormone produced in the adrenal cortex that also impacts metabolism, being a glucocorticoid that helps regulate metabolic processes.
















