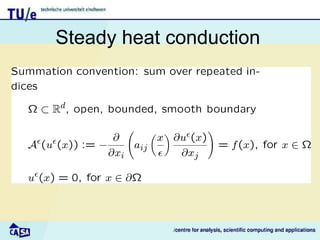
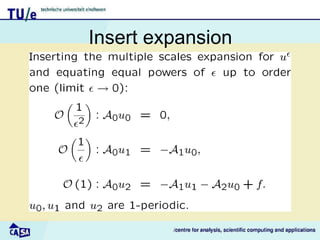
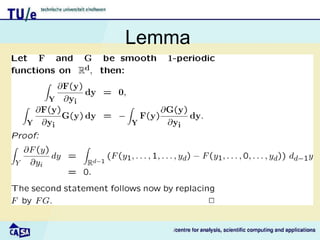
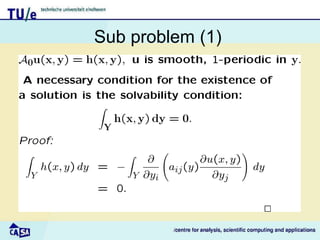
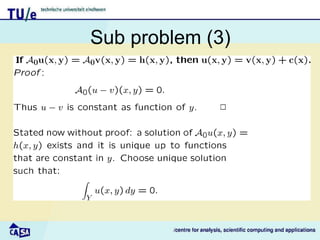
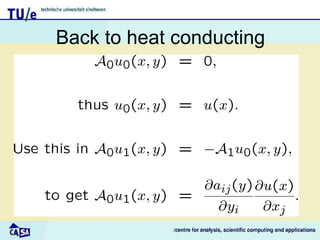
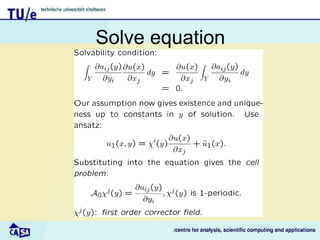
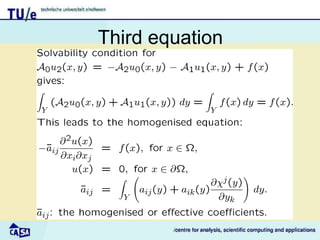
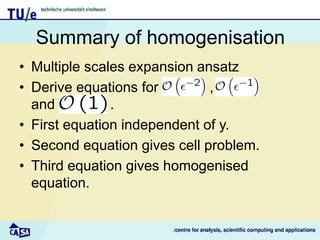
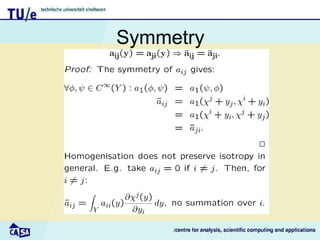
This document discusses homogenization theory for partial differential equations. Homogenization is used to derive a homogenized problem when there are multiple time or length scales involved. It works by treating the fast and slow scales independently. As an example, it goes through the process of homogenizing the steady state heat conduction equation. This involves a multiple scales expansion, deriving cell problems, and obtaining a homogenized equation with effective coefficients. The one dimensional case is examined in detail.