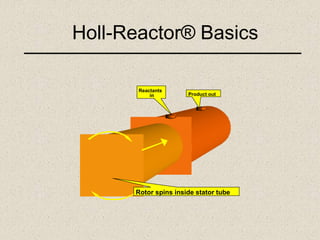
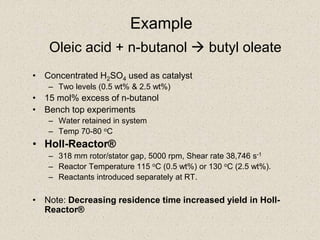
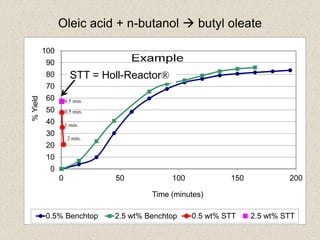
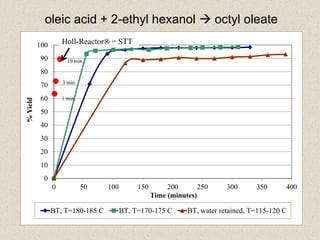
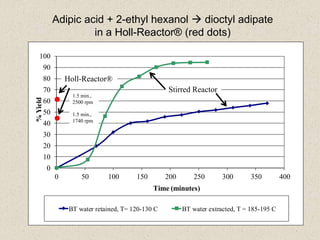
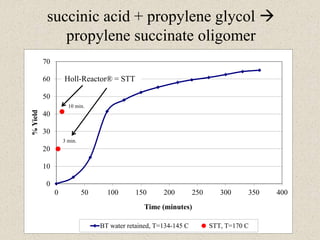
The document describes the Holl-Reactor, a two-dimensional reactor design that allows independent control of shear and flow rate. It offers improved reaction control and decreased reaction times, often by orders of magnitude. Several examples are given of reactions showing significantly faster reaction times in the Holl-Reactor compared to conventional stirred tank reactors. The Holl-Reactor enhances a variety of chemistries and can speed up reactions over 100 times.