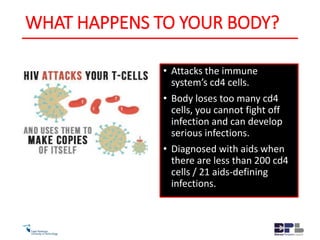
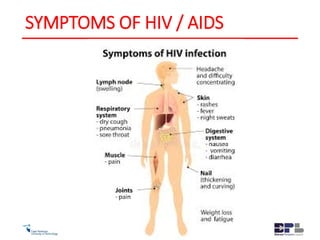
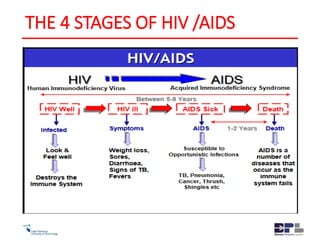
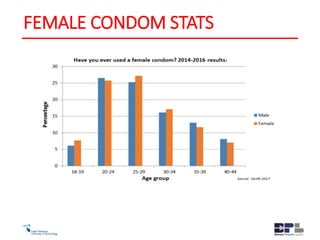
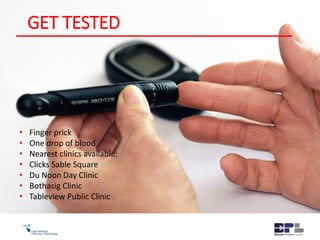
This document outlines the agenda and content for an HIV/AIDS awareness workshop. The workshop aims to break stigma, increase awareness, and encourage early testing and lifestyle changes. The agenda includes sessions on the history and transmission of HIV/AIDS, its impact on the body, myths, statistics in South Africa, new developments like PrEP, discrimination, and practical exercises. Objectives are to empower participants and increase understanding of the virus and challenges. The workshop covers topics like the origin of HIV, its evolution and spread, transmission methods, symptoms, treatment, stigma, and steps individuals can take to reduce risk and support others.