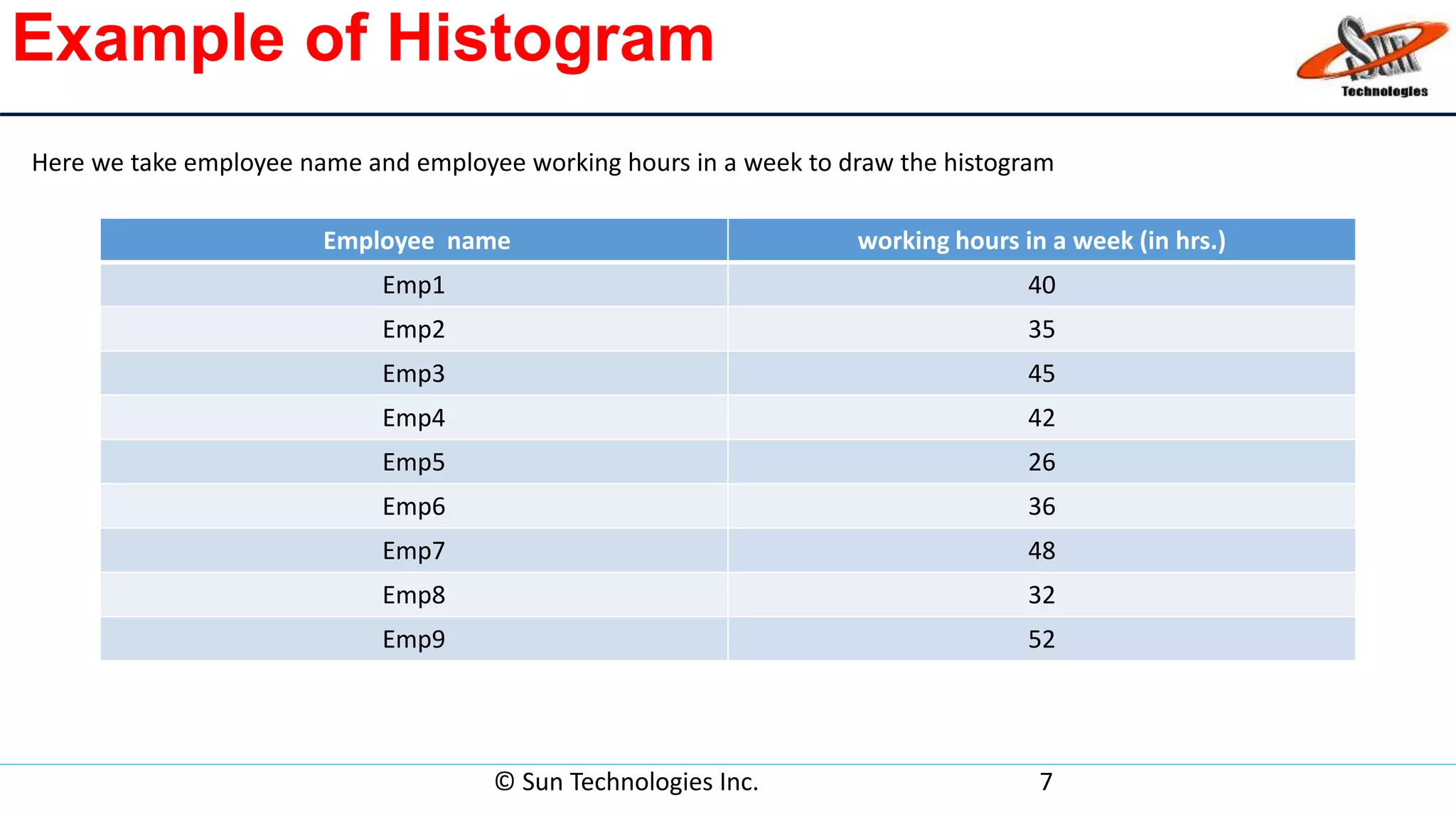
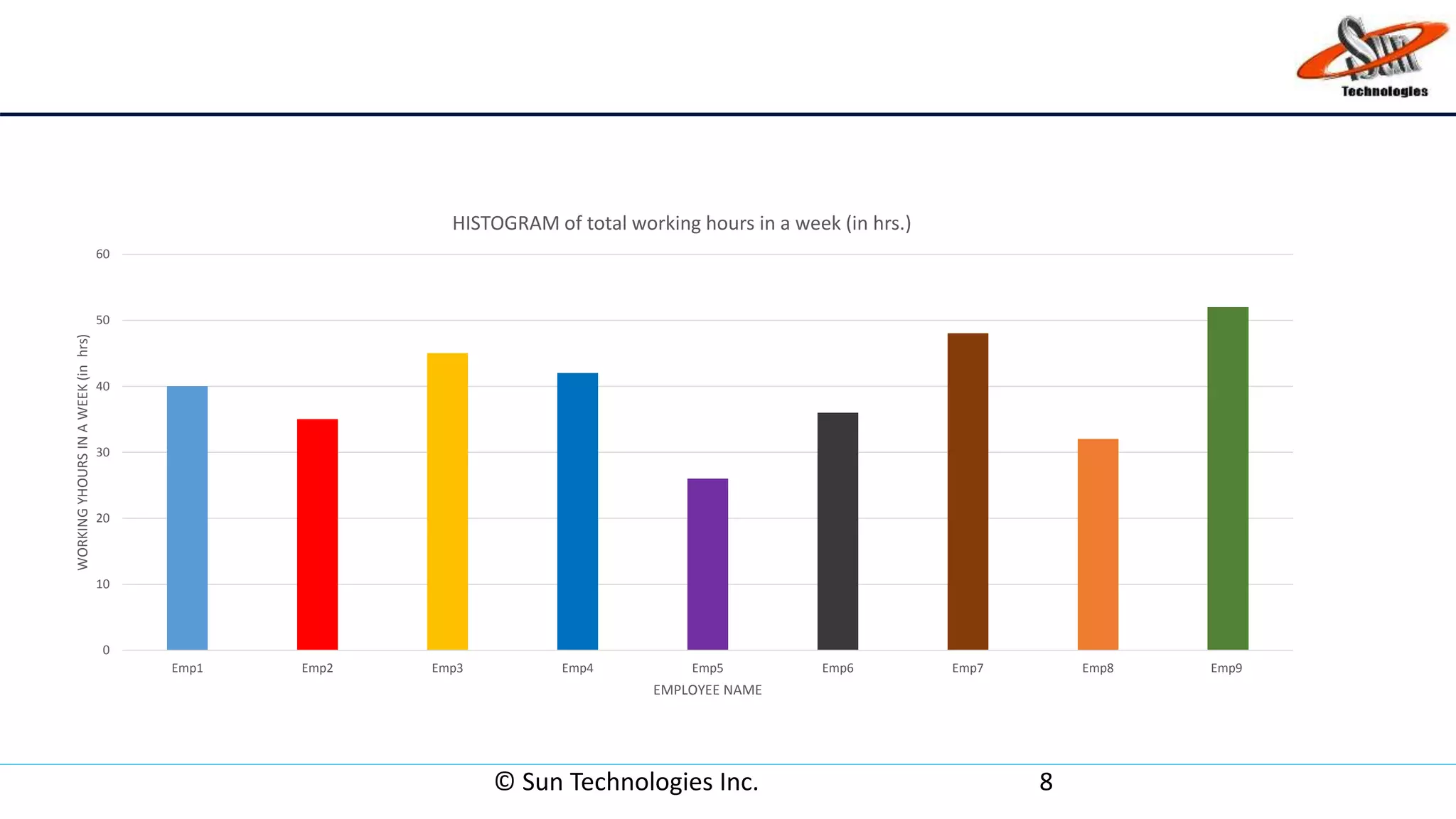
This document discusses histograms, which are graphical representations of frequency distributions of data presented as bar charts. It describes histograms as a quality tool that can summarize large data sets, compare measurements to specifications, and assist in decision making. The key parts of a histogram are identified as the title, horizontal axis, bars, and vertical axis. Steps for constructing a histogram are outlined, and an example histogram showing employee working hours is provided to illustrate the components. Advantages of histograms include displaying large amounts of data and revealing variations, while disadvantages are limitations to continuous data and difficulty comparing multiple data sets.