High temperature proton transport in BaCe0
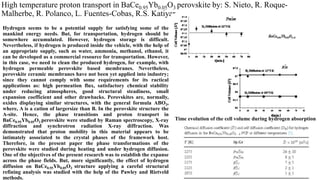
- 1. High temperature proton transport in BaCe0.95Yb0.05O3 perovskite by: S. Nieto, R. Roque- Malherbe, R. Polanco, L. Fuentes-Cobas, R.S. Katiyar. Hydrogen seems to be a potential supply for satisfying some of the mankind energy needs. But, for transportation, hydrogen should be somewhere accumulated. However, hydrogen storage is difficult. Nevertheless, if hydrogen is produced inside the vehicle, with the help of an appropriate supply, such as water, ammonia, methanol, ethanol, it can be developed as a commercial resource for transportation. However, in this case, we need to clean the produced hydrogen, for example, with hydrogen permeable perovskite based membranes. Nevertheless, perovskite ceramic membranes have not been yet applied into industry; since they cannot comply with some requirements for its ractical applications as: high permeation flux, satisfactory chemical stability under reducing atmospheres, good structural steadiness, small expansion coefficient and other drawbacks. Perovskites are, normally, oxides displaying similar structures, with the general formula ABO3, where, A is a cation of largersize than B. In the perovskite structure the A-site. Hence, the phase transitions and proton transport in BaCe0.95Yb0.05O3 perovskite were studied by Raman spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction and synchrotron radiation X-ray diffraction. Was demonstrated that proton mobility in this material appears to be intimately associated to the crystal phases of the framework host. Therefore, in the present paper the phase transformations of the perovskite were studied during heating and under hydrogen diffusion. One of the objectives of the present research was to establish the expanse across the phase fields. But, more significantly, the effect of hydrogen diffusion on BaCe0.95Yb0.05O3 structure applying a careful structural refining analysis was studied with the help of the Pawley and Rietveld methods. Time evolution of the cell volume during hydrogen absorption
