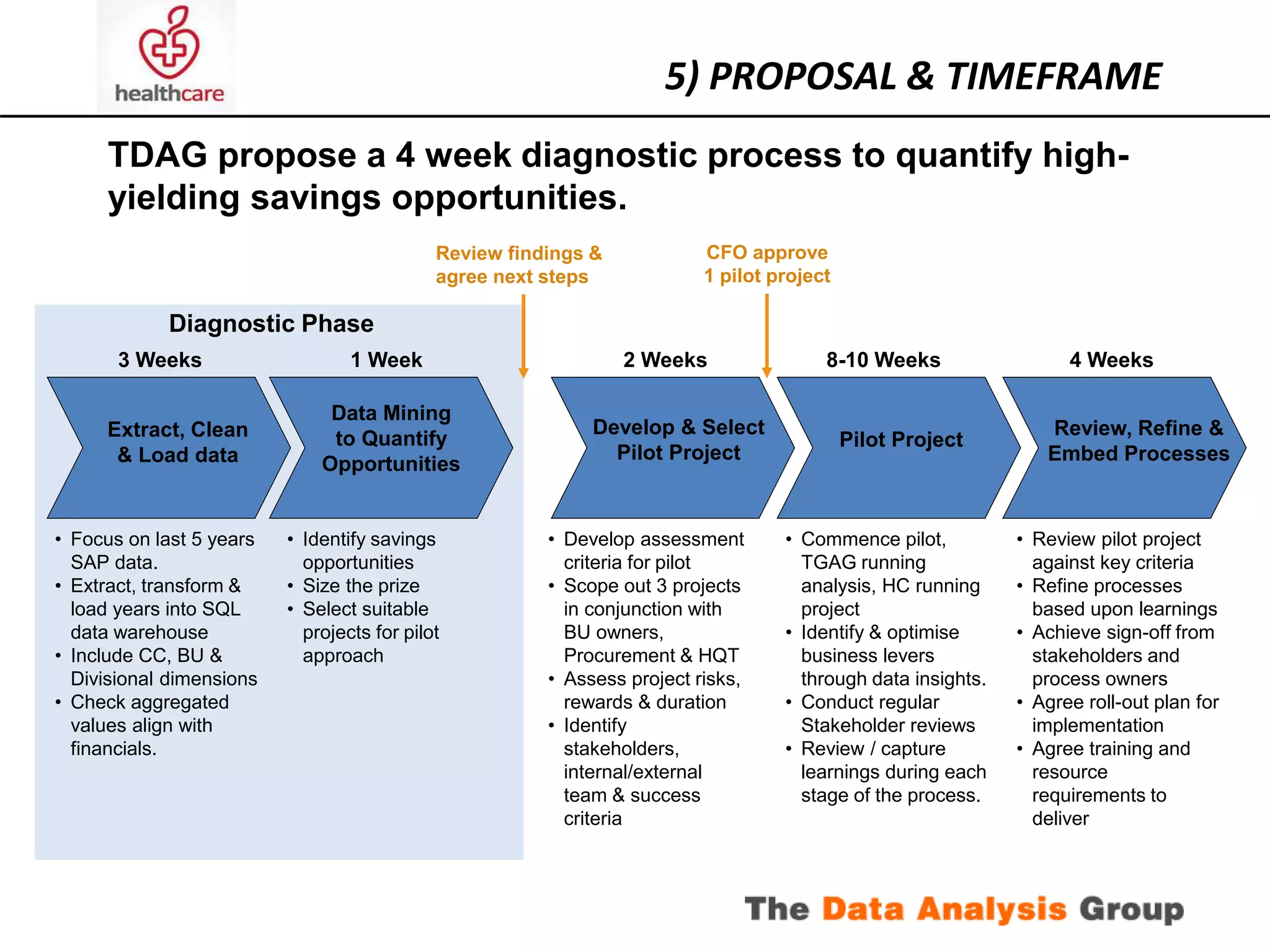
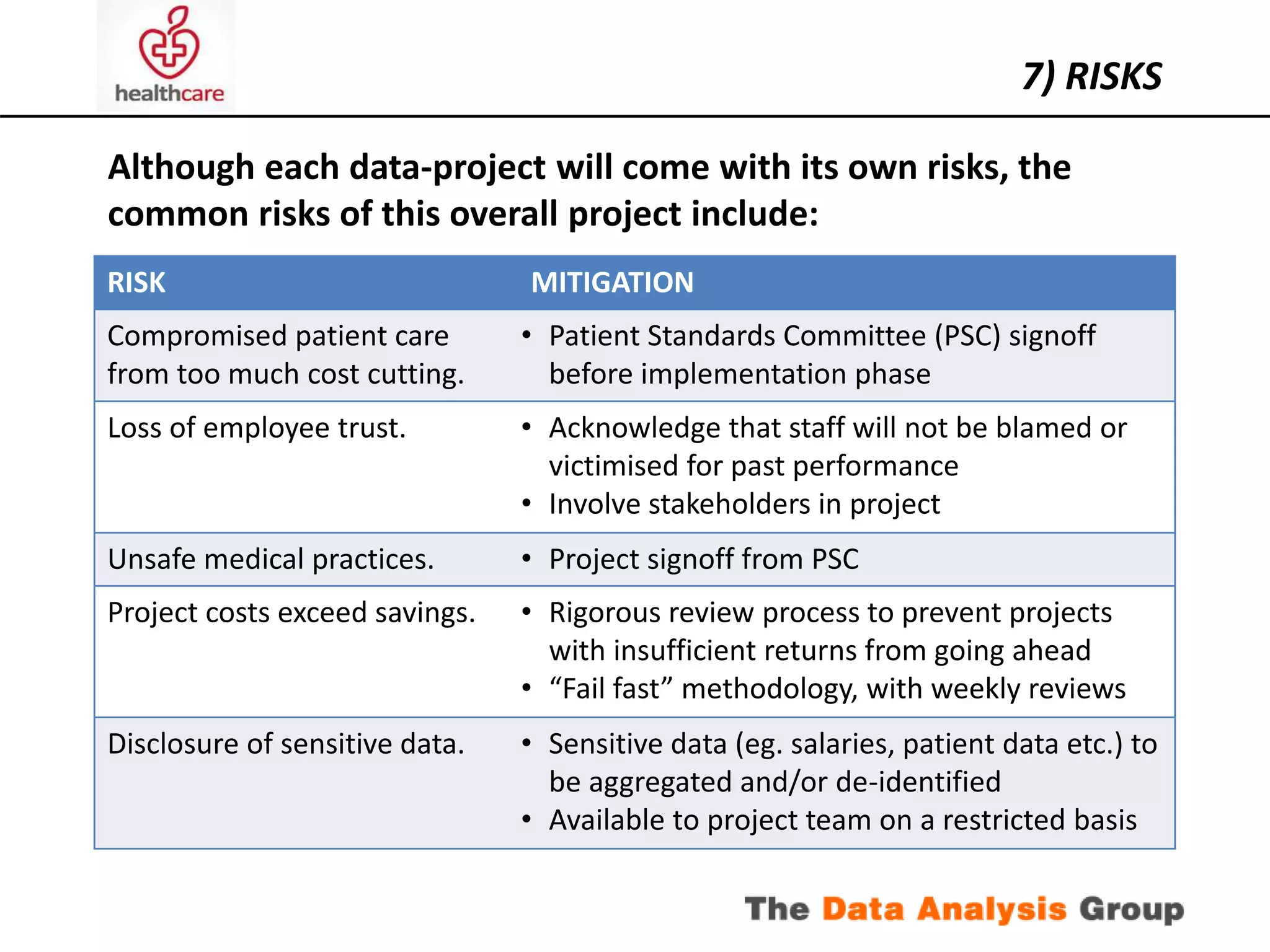
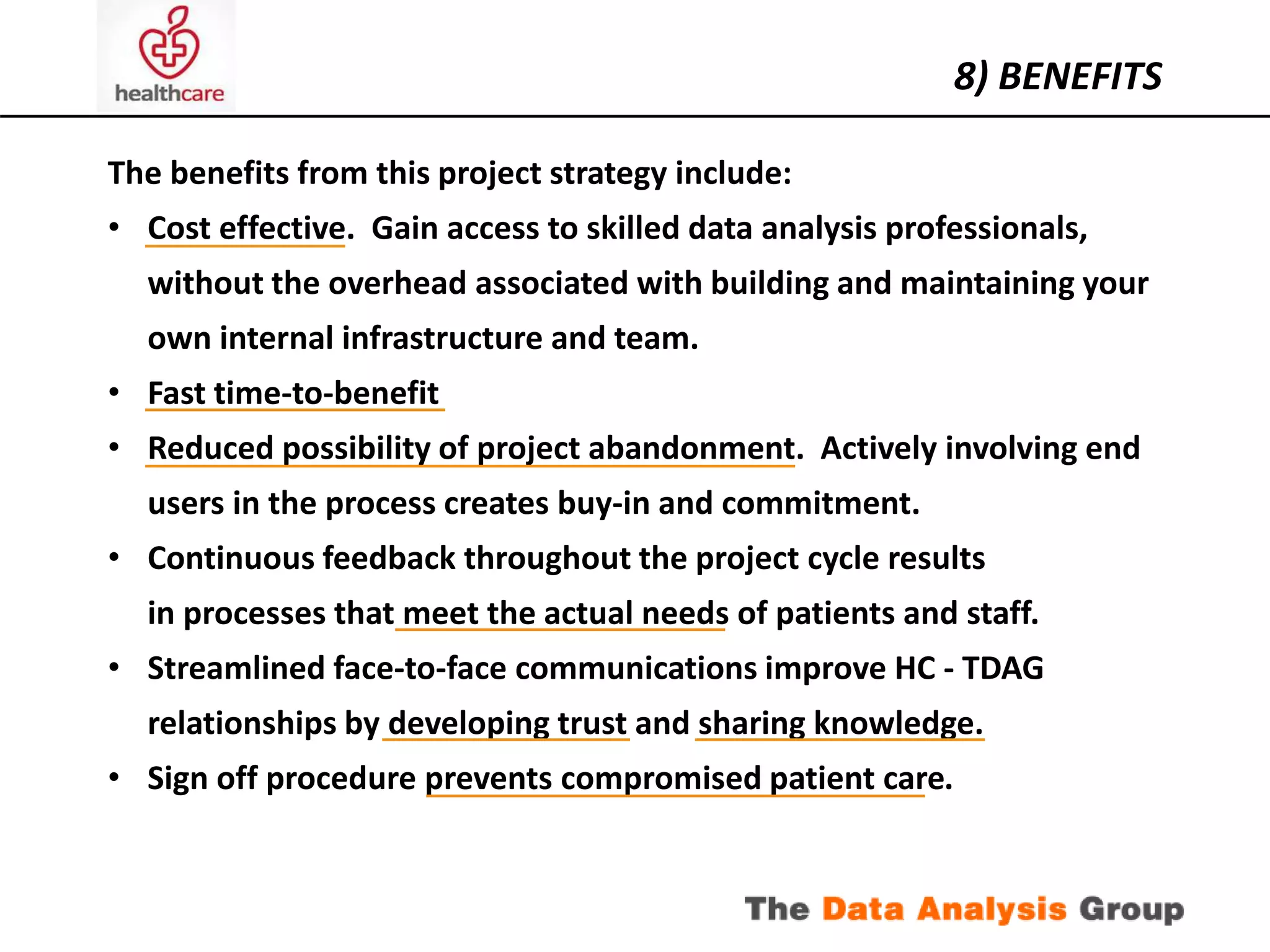
The document outlines a proposed project to achieve cost reductions through advanced data analytics in a healthcare setting, focusing on optimizing operations and improving patient care. It includes an analysis of current data sources, skills, and systems, as well as identified potential savings opportunities and a structured approach for implementation. Key components involve stakeholder engagement, risk management, and the establishment of a pilot project to explore high-yielding savings opportunities.