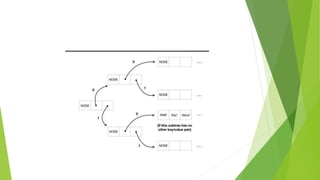
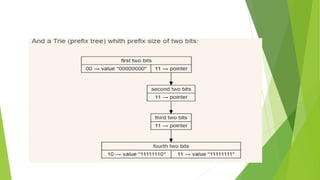
A hash array mapped trie (HAMT) is an implementation of an associative array that combines the characteristics of a hash table and an array mapped trie. It achieves almost hash table-like speed while using memory more economically by hashing keys to ensure even distribution and storing a bitmap indicating non-nil pointers followed by a pointer array of that length at each node. Implementation involves using the population count function to count ones in a number's binary representation, available in some instruction sets and languages.