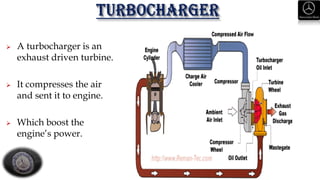
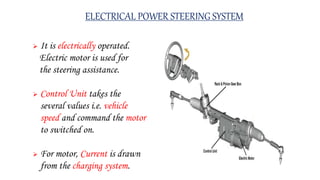
This document provides an overview of Mercedes-Benz vehicles, including:
- The history and origins of Mercedes-Benz dating back to Karl Benz and Gottlieb Daimler in the late 1800s.
- Details on Mercedes-Benz production facilities located in India.
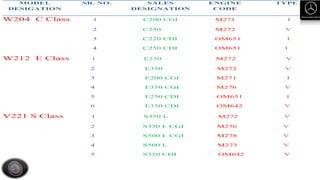
- Explanations of Mercedes-Benz vehicle nomenclature, models, innovations, body styles, and identification codes.
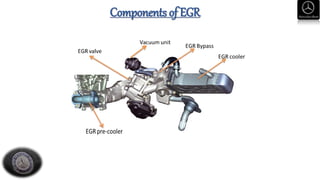
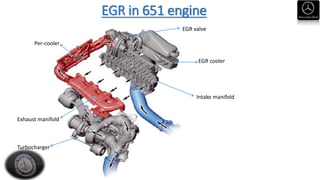
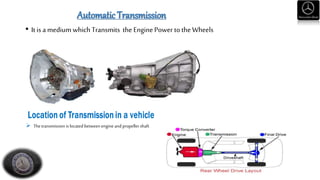
- Descriptions of engine designations, maintenance procedures, and inspection points for key vehicle systems.