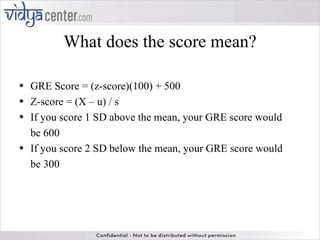
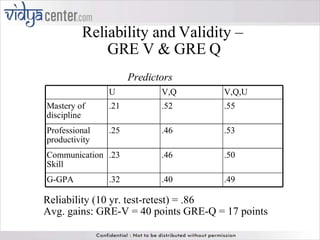
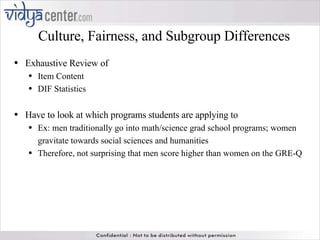
The GRE (Graduate Record Examination) measures analytical writing, verbal reasoning, and quantitative reasoning skills, with scores reported on distinct scales for each section. It highlights the importance of not solely relying on GRE scores for student admissions and emphasizes the use of additional factors like GPA and personal statements. The document also explains the differences between paper-and-pencil and computerized testing formats, alongside various test-taking strategies and considerations of reliability and validity across demographic groups.