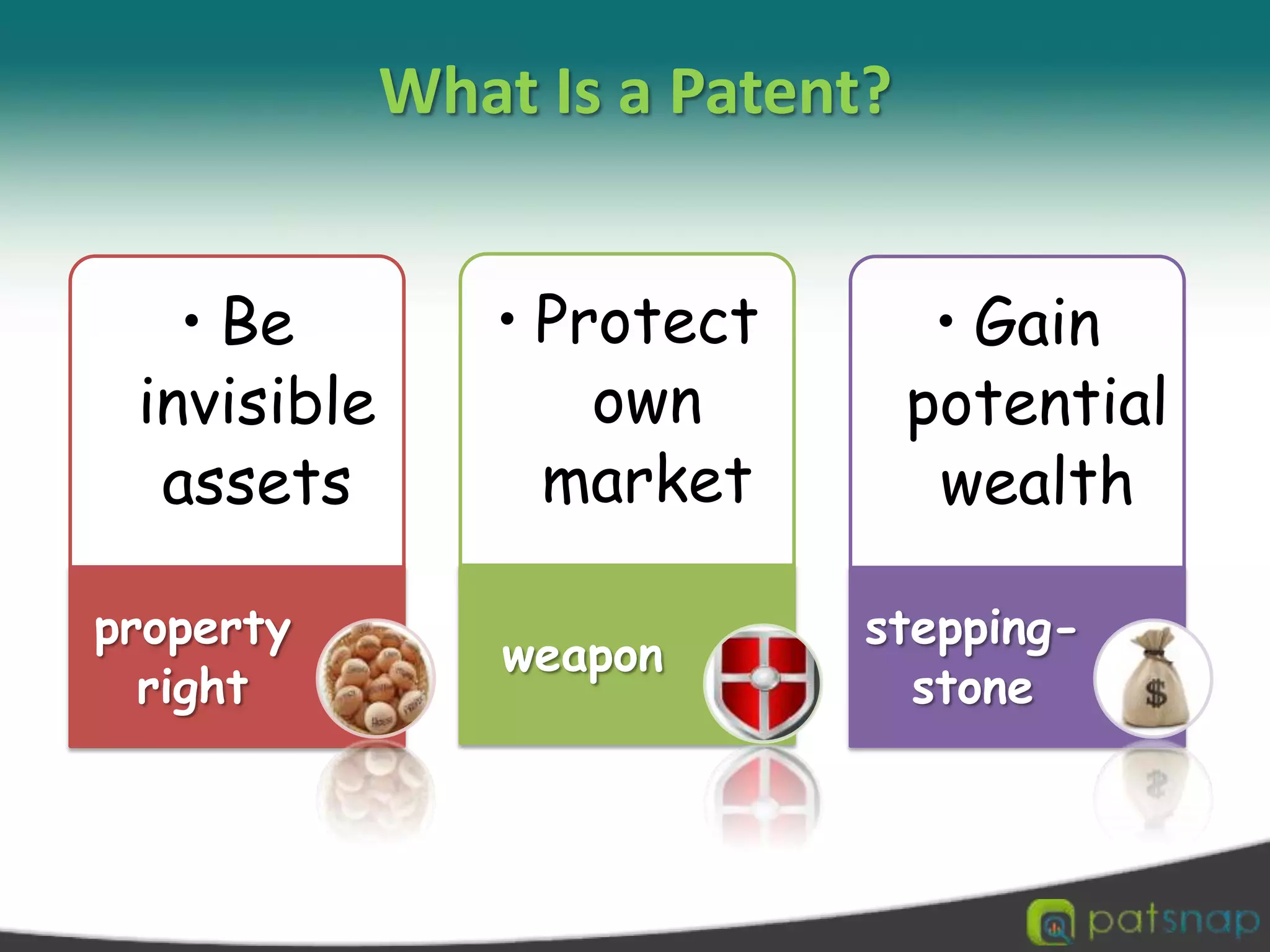
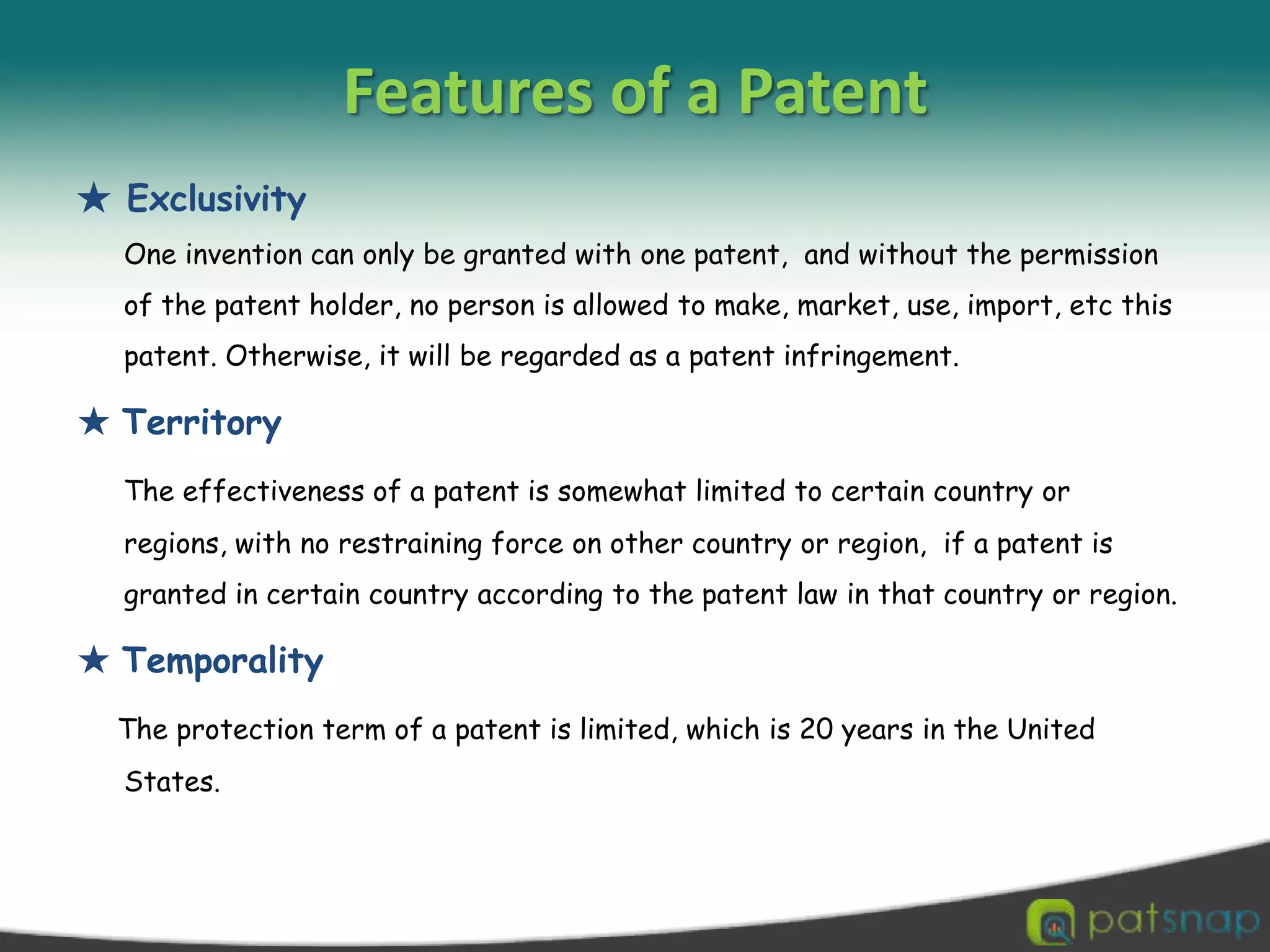
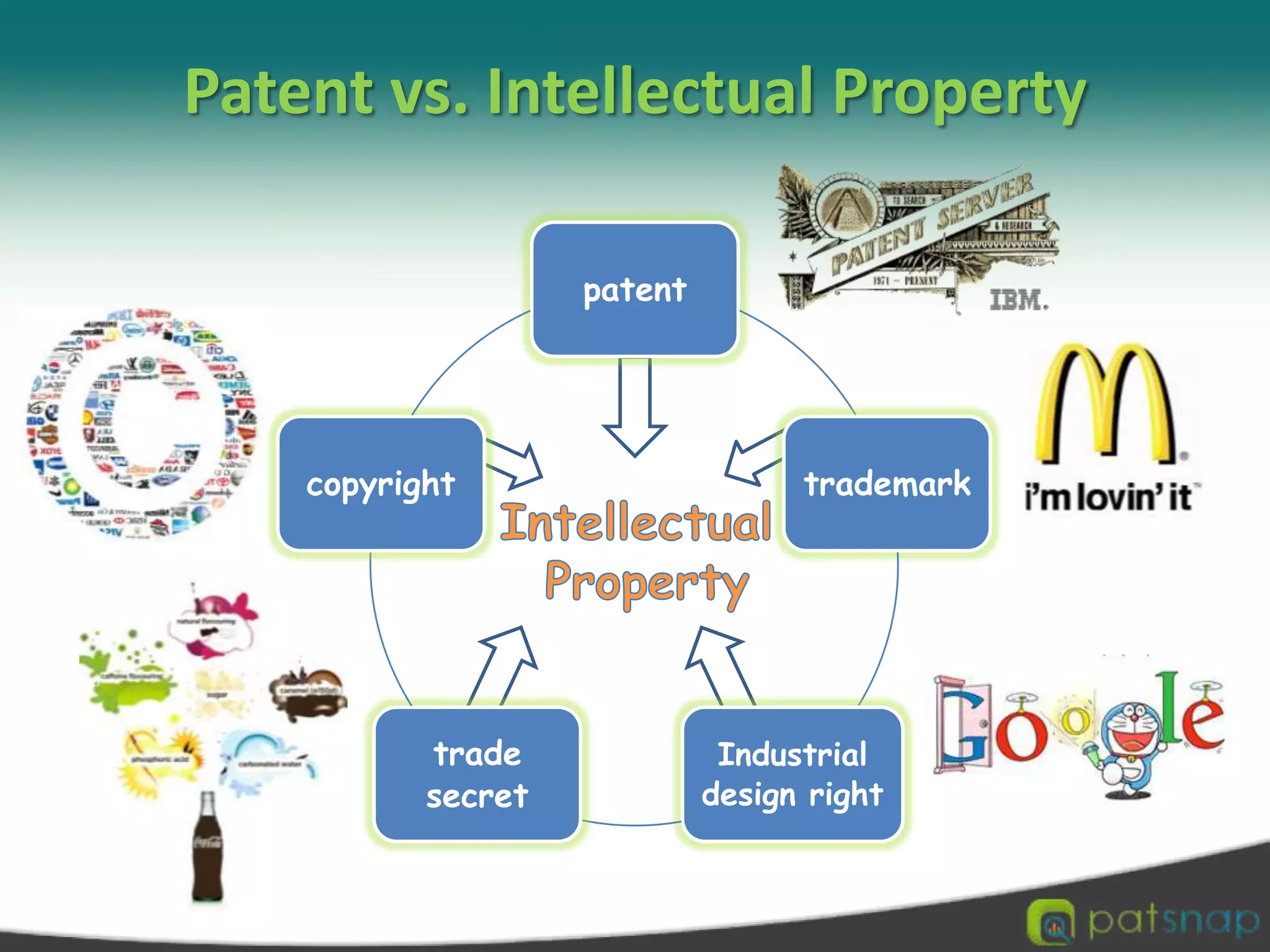
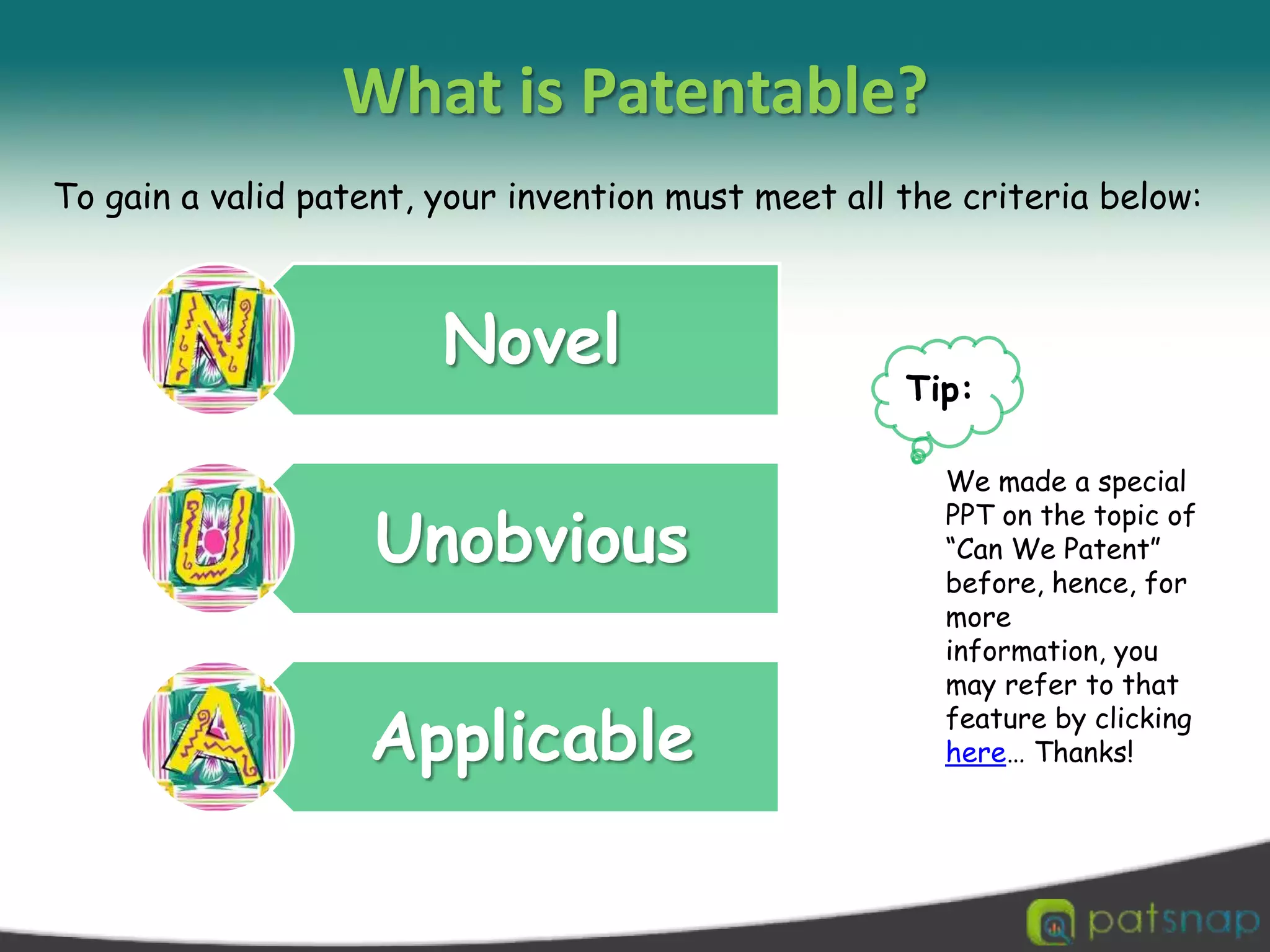
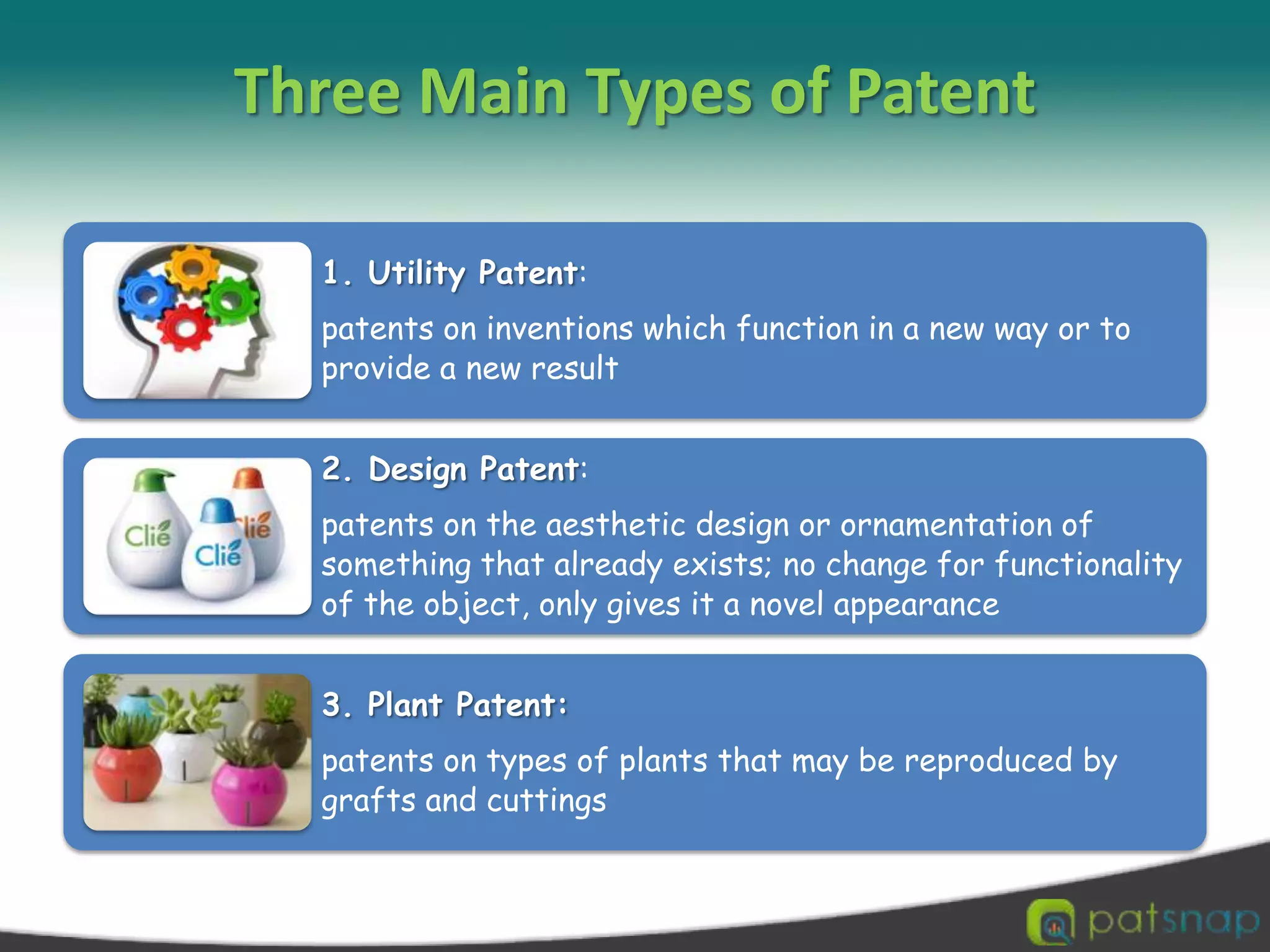
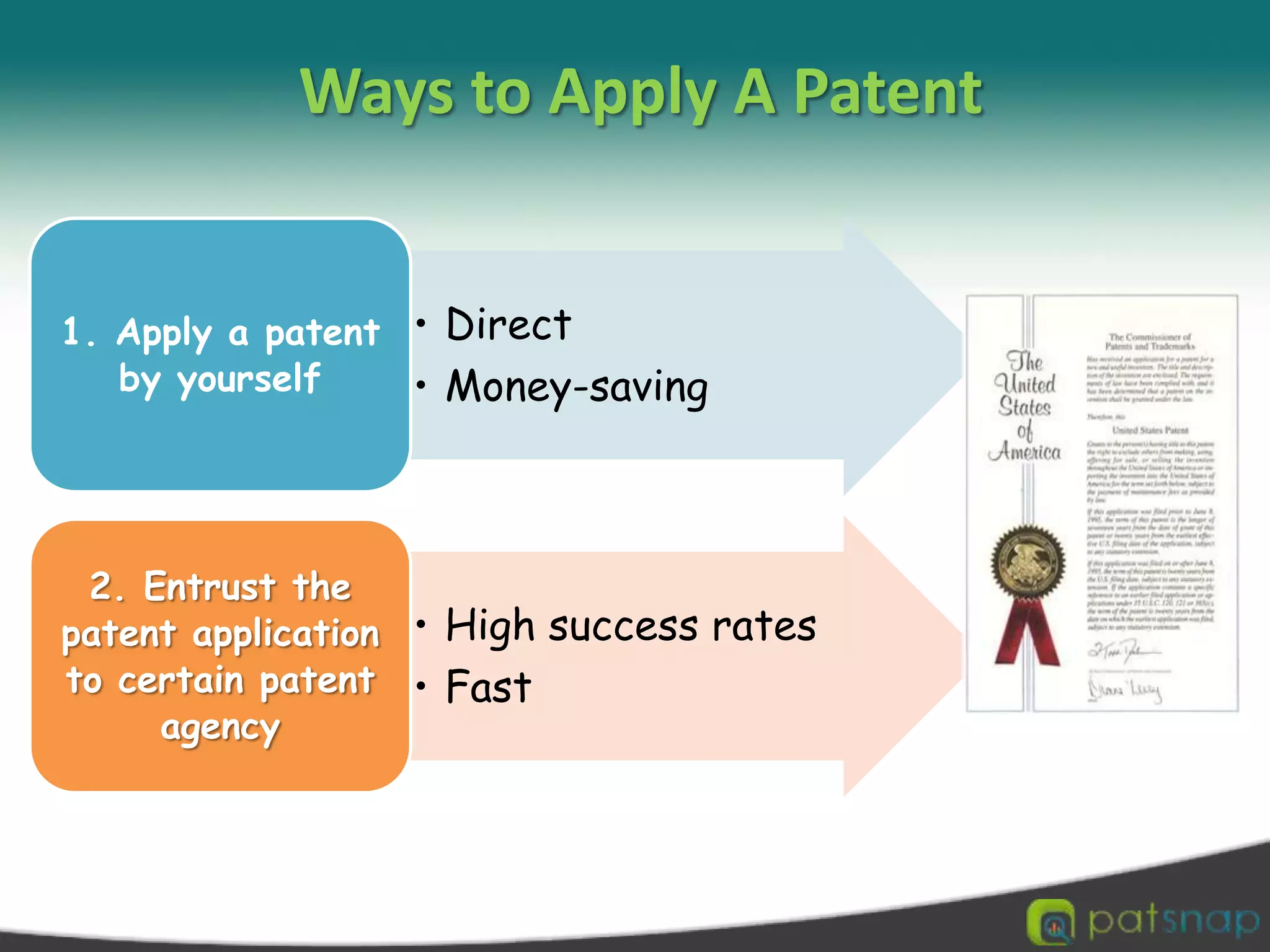
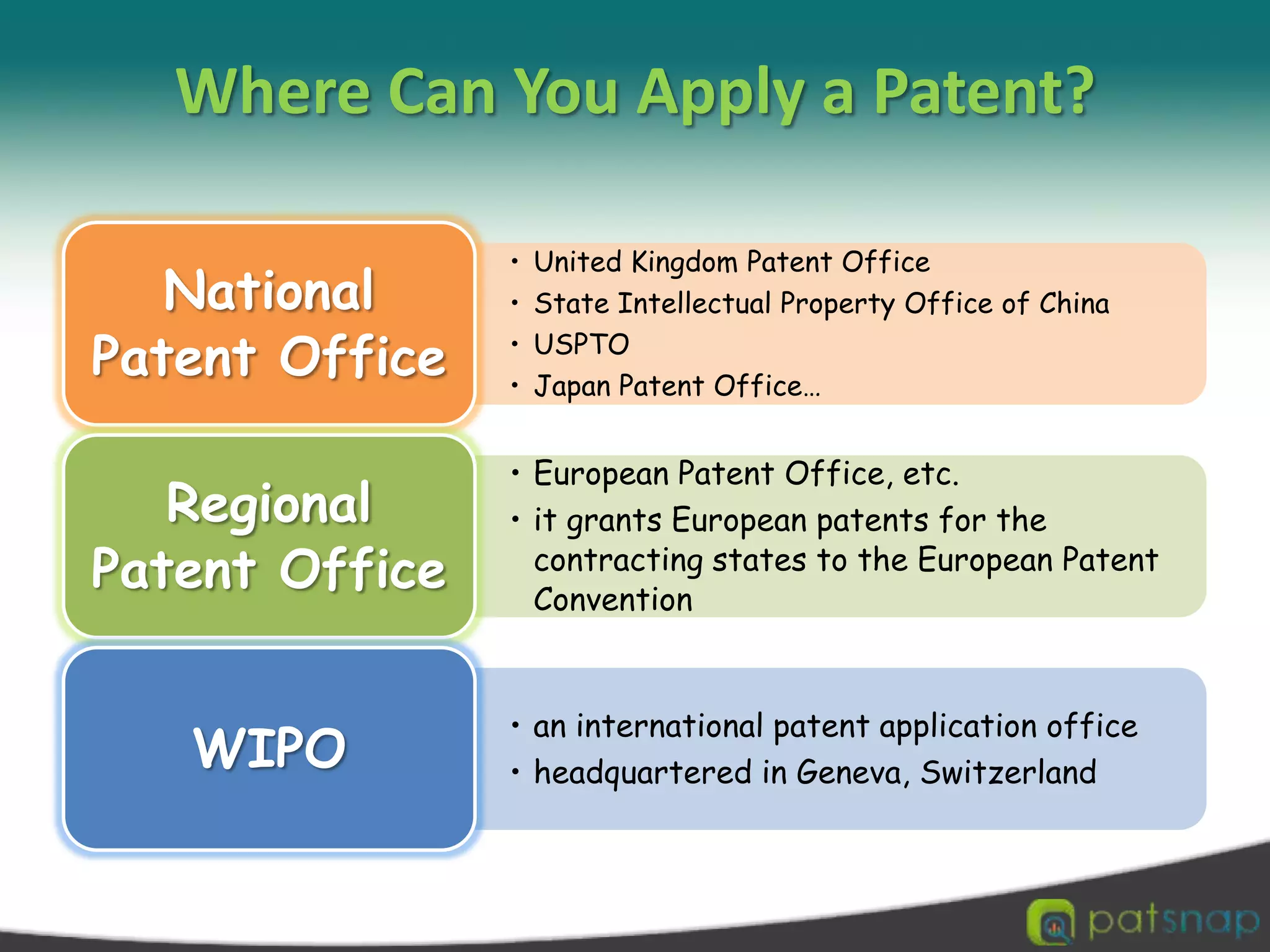
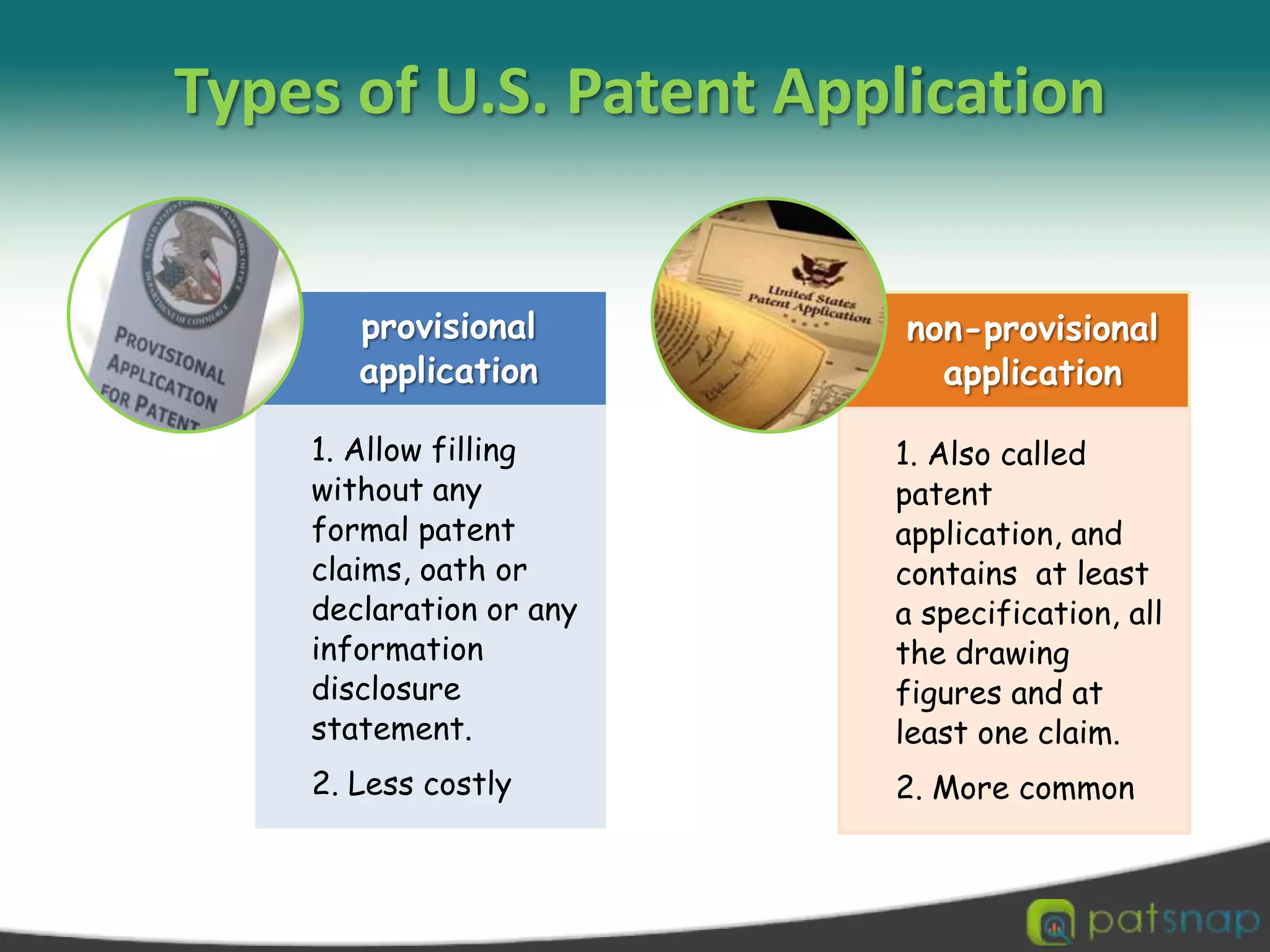
A patent is a set of exclusive rights granted by a national government to anyone who invents or discovers any new and useful process, machine, article of manufacture, or composition of matter. There are three main types of patents: utility patents, design patents, and plant patents. Patents provide exclusivity, territorial limits, and a limited term of protection, usually 20 years. While intellectual property encompasses various creations of the mind like copyrights and trademarks, a patent specifically protects inventions. The criteria for an invention to be patentable include being novel, non-obvious, and useful. Patents can be applied for through national patent offices and the Patent Cooperation Treaty provides an international application process.